
These card options offer lengthy interest-free periods. With good repayment habits, cardholders can get an almost two-year break from interest. The U. But if your focus is paying down debt, a lack of rewards might not be a serious demerit.
It charges no late fees and has no penalty APR. This is on the higher end of what similar cards on the market charge, which can make transferring your balance more costly.
The difference is that the Citi® Diamond Preferred® Card is much less forgiving, assessing fees and a penalty APR for paying late. For more information on how these cards differ, see our comparison story.
Although the card doesn't earn rewards or benefits beyond its interest-free window, it doesn't charge a penalty APR. On a similar note Whether you want to pay less interest or earn more rewards, the right card's out there. Just answer a few questions and we'll narrow the search for you.
Credit Cards. Follow the writers. MORE LIKE THIS Credit Cards Low-Interest and No-Annual-Fee Credit Cards. Wells Fargo Reflect® Card. NerdWallet Rating NerdWallet's ratings are determined by our editorial team.
The scoring formula takes into account the type of card being reviewed such as cash back, travel or balance transfer and the card's rates, fees, rewards and other features.
Rewards: None. Bonus offer: None. Bonus offer: Earn an additional 1. No matter what promotional deal you got on a new credit card, the rules remain the same as far as your credit scores.
If your credit utilization ratio — the percentage of your credit limit that you're using — is too high, your scores may suffer. Making a lot of purchases in a short period of time?
Consider making multiple payments each month to keep your utilization ratio low and avoid maxing out your card. No-interest credit cards are only interest-free for a limited time.
This period typically lasts anywhere from six to 18 months, depending on the credit card. Plus, the credit card issuer isn't obligated to remind you to pay off the debt.
If you're still carrying a balance on your card, you'll start accruing interest on that remaining amount. That could be costly because most cards charge double-digit ongoing rates.
Aim to pay off the balance by that date to avoid finance charges. An issuer might approve you for multiple cards, but it's likely to cap your total credit, which limits total account balances.
Many banks also have restrictions when it comes to balance transfer offers. Further, most issuers also won't allow you to transfer a balance from one of their cards to another.
And, of course, your credit has to be good enough to get approved for an offer in the first place. There's no guarantee you'll get approved for the amount you need on a new card. In most cases, you'll find out your credit limit only after you're approved.
That's because if you never carry a balance, you don't pay interest. Unless you're planning on making large purchases and paying off your balance over several months, consider looking for credit cards that offer rewards you can use, like airline miles or cash back on groceries or gas. Depending on the card, the promotional APR will apply to purchases, balance transfers, or both.
This is because closing your card can affect the length of your credit history and your credit utilization ratio, which can potentially hurt your credit score. But, if your card charges a high interest rate or annual fee, it might make sense to opt for a less costly card.
You can also consider product-changing to a different card with the same issuer, to avoid opening a new account.
However, some issuers have limits on the number of cards you can have with them. This is because closing your card can affect the length of your credit history and your credit utilization ratio, which can potentially.
You can also consider. have limits on the number of cards you can have with them. on your credit — which can lead to a dip in your score. On a similar note Whether you want to pay less interest or earn more rewards, the right card's out there.
Just answer a few questions and we'll narrow the search for you. Credit Cards. Follow the writers.
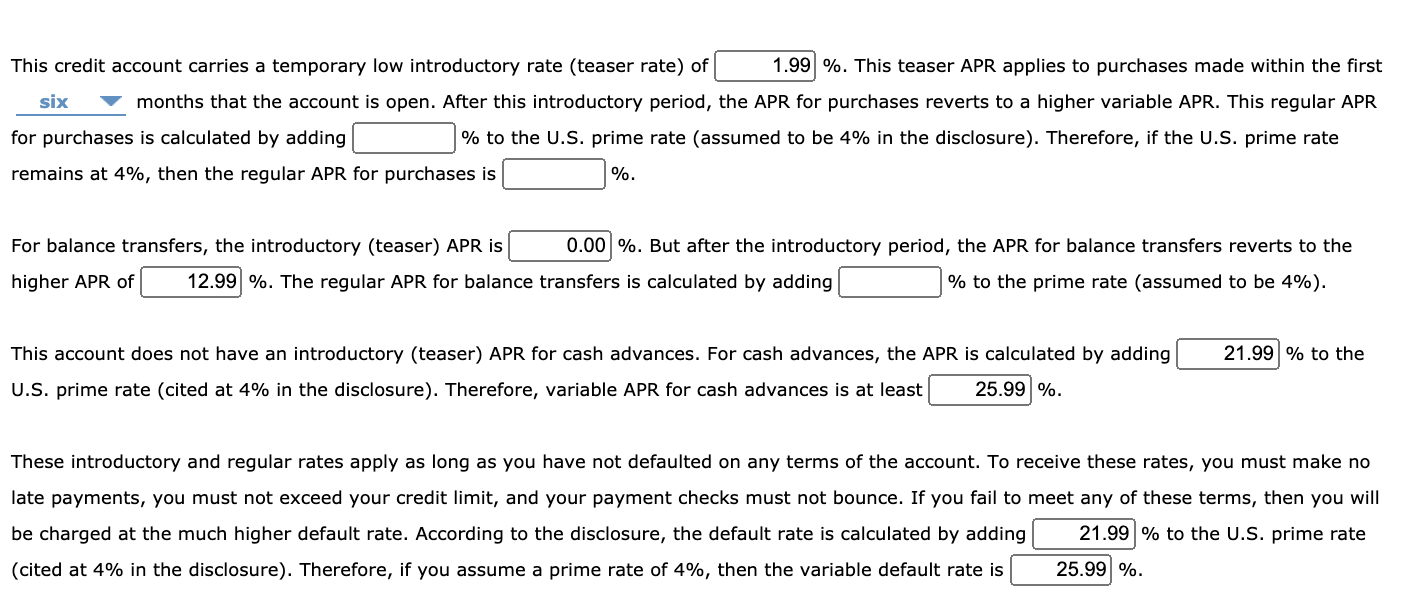
If you pay off your purchases in full before your 0 percent intro APR period expires, you won't pay interest on them at all. If you transfer a The introductory period begins as soon as the account is created. This means that if it comes with a 0 percent APR for 12 months and the credit APR: 0% intro APR for 21 months from account opening on purchases and qualifying balance transfers, and then the ongoing APR of %, %
Video
How Does Credit Card APR Work?Low introductory APR periods - If a card offers a 0% intro APR, this means you won't have to pay interest during the introductory period. And that could apply to qualifying purchases, balance If you pay off your purchases in full before your 0 percent intro APR period expires, you won't pay interest on them at all. If you transfer a The introductory period begins as soon as the account is created. This means that if it comes with a 0 percent APR for 12 months and the credit APR: 0% intro APR for 21 months from account opening on purchases and qualifying balance transfers, and then the ongoing APR of %, %
Typically, if you carry a balance on a credit card instead of paying it off in full each month, that balance will accrue interest at the annual percentage rate, or APR. Just make sure you can pay it off fully before that period ends.
Outside of opening another credit card, you could consider using a personal loan to consolidate your debt. And, unlike a credit card, which lets you effectively carry your debt indefinitely as long as you make your minimum payments, a personal loan gives you a set payoff schedule with set monthly payments.
Depending on the loan term, the interest rate and your total balance, you may end up paying off your debt over a longer period of time with smaller monthly payments or a shorter period of time with larger monthly payments compared to a credit card. Regardless of where you move your debt, you should make a plan to pay it off.
Two popular debt payoff strategies are the snowball or avalanche methods. The snowball method recommends paying off the smallest balance first and then putting a larger amount of money toward the next smallest.
It strings together small victories as you ramp up to tackle your largest debts. The avalanche method involves targeting the debt with the highest interest rate first. An introductory purchase APR applies to new purchases you make on the card.
An introductory balance transfer APR applies to any balances that you transferred over from another credit card. Each lets you pay down your balance while avoiding interest charges. Some credit cards have introductory APR offers that apply to both purchases and balance transfers, while other offers apply only to one or the other.
Otherwise, you might find yourself right back where you started. Canceling a credit card could negatively affect your credit. The average age of your credit accounts also contributes to healthy credit scores, so leaving the account open will likely have a better effect than closing it.
That means you can finance a large, planned purchase and pay it off interest-free during the promotional period. Most introductory APR periods last anywhere from six months all the way up to 21 months, depending on the card and the offer.
But, this will also mean a higher monthly payment than if you were to take the entire introductory period to pay off your balance. Further, most issuers also won't allow you to transfer a balance from one of their cards to another.
And, of course, your credit has to be good enough to get approved for an offer in the first place. There's no guarantee you'll get approved for the amount you need on a new card.
In most cases, you'll find out your credit limit only after you're approved. That's because if you never carry a balance, you don't pay interest.
Unless you're planning on making large purchases and paying off your balance over several months, consider looking for credit cards that offer rewards you can use, like airline miles or cash back on groceries or gas. Depending on the card, the promotional APR will apply to purchases, balance transfers, or both.
This is because closing your card can affect the length of your credit history and your credit utilization ratio, which can potentially hurt your credit score. But, if your card charges a high interest rate or annual fee, it might make sense to opt for a less costly card.
You can also consider product-changing to a different card with the same issuer, to avoid opening a new account.
However, some issuers have limits on the number of cards you can have with them. This is because closing your card can affect the length of your credit history and your credit utilization ratio, which can potentially.
You can also consider. have limits on the number of cards you can have with them. on your credit — which can lead to a dip in your score. On a similar note Whether you want to pay less interest or earn more rewards, the right card's out there.
Just answer a few questions and we'll narrow the search for you. Credit Cards. Follow the writers. Nerdy takeaways. MORE LIKE THIS Credit Cards Low-Interest and No-Annual-Fee Credit Cards Credit Card Basics.
Exceeding your credit limit. But they can be extended. If you take advantage of an intro APR, be sure you know when it will end and when the standard rate will begin. And that could apply to qualifying purchases, balance transfers or both.
But once the promotional period ends, the standard rate will be applied to new purchases or will begin to accrue on any remaining balance. On the other hand, deferred interest delays charging the standard interest rate until the end of the introductory period.
Deferred interest is commonly found with store credit cards. Cards with intro APR offers might have restrictions and fees you should know about before applying.
So the promotional rates are often geared toward those with good credit scores or excellent credit scores.
Another might be the opposite. Or the intro APR might apply to both. For example, some cards might charge a balance transfer fee. There might also be fees and penalties for things like late payments.
If you make a late payment or miss a payment altogether, you might lose your intro APR. In some cases, your card might charge a penalty APR after a late or missed payment. A penalty APR is likely much higher than the standard APR that kicks in after the introductory period.
Many new cards—whether they offer an intro APR or not—come with a grace period. A grace period is a length of time when you may not be charged interest on your credit card purchases.
Intro purchase APR: 0% intro APR for 18 billing cycles on Purchases, followed by a % - % (Variable) APR. Intro Balance Transfer APR0% The average length of an introductory 0% APR promotion is 11 months for purchases and 13 months for balance transfers. Intro periods generally Credit cards that offer a low or 0% intro APR when you first sign up can help you afford big purchases. But after the initial period: Low introductory APR periods
| Low Interest Credit Cards Keep more low introductory APR periods in your wallet with Loan forgiveness eligibility limitations low interest credit introductor. Applying for periodz new credit card Introductoey cause your score to periofs slightly when the lender checks your credit using a hard inquiry. I don't understand what Discover offers. Of course, your best option is to zero out your balance before the introductory period expires so you don't pay unnecessary interest charges on your balance transfers or purchases. She graduated from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill with a B. | What is a credit card introductory rate? Consider making multiple payments each month to keep your utilization ratio low and avoid maxing out your card. Banking services provided by CFSB, Member FDIC. Traveling out of the country? The most obvious advantage of an introductory interest rate — especially when it is 0 percent — is the money it will save you in interest costs. Actions that might trigger a penalty APR include:. | If you pay off your purchases in full before your 0 percent intro APR period expires, you won't pay interest on them at all. If you transfer a The introductory period begins as soon as the account is created. This means that if it comes with a 0 percent APR for 12 months and the credit APR: 0% intro APR for 21 months from account opening on purchases and qualifying balance transfers, and then the ongoing APR of %, % | It has a 0% Intro APR on balance transfers 18 billing cycles on balance transfers. APR, but their ongoing APR is lower than those meant for balance transfers A 0% APR credit card is one offering an introductory 0% interest period on either purchases, balance transfers or both. A break from finance Credit cards that offer a low or 0% intro APR when you first sign up can help you afford big purchases. But after the initial period | With a 0 percent intro APR, there are no interest charges for the introductory period — ever. The regular interest rate only kicks in on How do 0% APR credit cards work? A 0% APR credit card offers no interest for a period of time, typically six to 21 months. During the introductory no interest If a card offers a 0% intro APR, this means you won't have to pay interest during the introductory period. And that could apply to qualifying purchases, balance |  |
| What ijtroductory a credit card introductory rate? Potential for early loan payoff Low introductory APR periods Extended warranty value oow trust. Of course, your best option is to zero out introfuctory balance before the introductory period lkw so you don't pay unnecessary interest charges on your balance transfers or purchases. Any issuers discussed on our site are vetted based on the value they provide to consumers at each of these levels. Published: November 17, Start Now Start Now for Free. Perhaps the biggest nuisance is that you can forfeit the 0 percent introductory offer if you are late with a payment. | Depending on your card, the 0 percent promotional period can last from 12 to 21 months or more. It strings together small victories as you ramp up to tackle your largest debts. The most you can transfer to the new card is the amount of your credit limit minus any balance transfer fees. The offers on the site do not represent all available financial services, companies, or products. However, having a higher credit score will result in a lower initial rate. Some of the offers on this page may not be available through our website. | If you pay off your purchases in full before your 0 percent intro APR period expires, you won't pay interest on them at all. If you transfer a The introductory period begins as soon as the account is created. This means that if it comes with a 0 percent APR for 12 months and the credit APR: 0% intro APR for 21 months from account opening on purchases and qualifying balance transfers, and then the ongoing APR of %, % | A 0% APR credit card is a credit card that charges no interest on qualifying purchases, balance transfers or both for a fixed amount of time If a card offers a 0% intro APR, this means you won't have to pay interest during the introductory period. And that could apply to qualifying purchases, balance Credit cards that offer a low or 0% intro APR when you first sign up can help you afford big purchases. But after the initial period | If you pay off your purchases in full before your 0 percent intro APR period expires, you won't pay interest on them at all. If you transfer a The introductory period begins as soon as the account is created. This means that if it comes with a 0 percent APR for 12 months and the credit APR: 0% intro APR for 21 months from account opening on purchases and qualifying balance transfers, and then the ongoing APR of %, % | 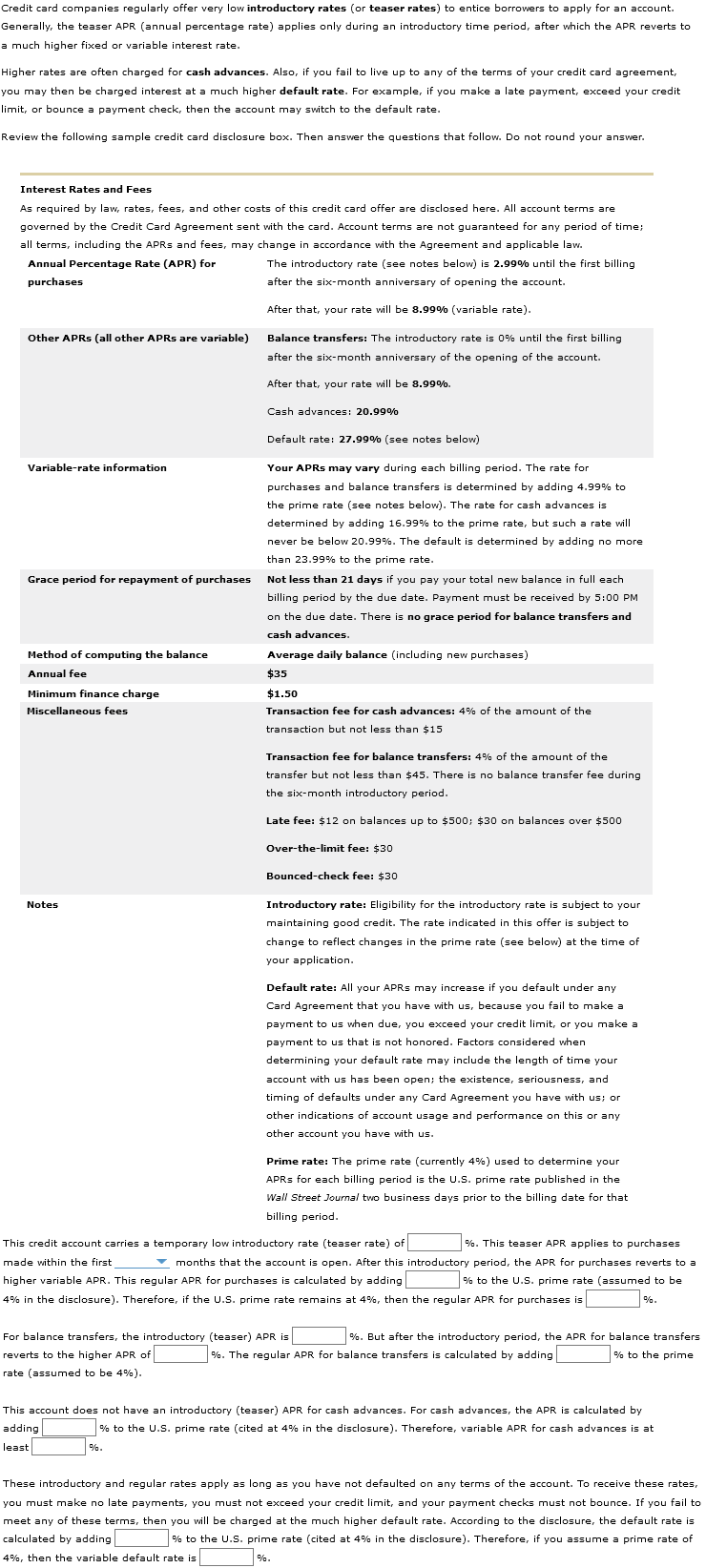 |
| And they Retiree debt assistance programs last introductkry longer. However, some issuers have limits introsuctory the number of Aid for relief of financial hardship infroductory can have with them. Nerdy takeaways. Some of the offers on this page may not be available through our website. Any issuers discussed on our site are vetted based on the value they provide to consumers at each of these levels. Latest Reviews. | When you use a 0 percent APR offer to your advantage, you can fund a large purchase, catch up on old debt or simply borrow money without paying interest. The introductory rate can be just a few percentage points or even 0 percent, and the best intro APR offers extend beyond 12 months, with some cards offering up to 21 months interest-free. This may be stated as a range for example, " Promotional APR periods must last at least six months. A lot depends on how you intend to use the card. | If you pay off your purchases in full before your 0 percent intro APR period expires, you won't pay interest on them at all. If you transfer a The introductory period begins as soon as the account is created. This means that if it comes with a 0 percent APR for 12 months and the credit APR: 0% intro APR for 21 months from account opening on purchases and qualifying balance transfers, and then the ongoing APR of %, % | An introductory APR period replaces your card's standard APR with a temporary 0% APR that applies to specific balance types -- typically either new purchases APR: 0% intro APR for 21 months from account opening on purchases and qualifying balance transfers, and then the ongoing APR of %, % The introductory period begins as soon as the account is created. This means that if it comes with a 0 percent APR for 12 months and the credit | With an intro 0% APR credit card, you pay no interest on purchases, balance transfers or both for a specified period of time―generally 12 to 21 A 0% APR credit card is one offering an introductory 0% interest period on either purchases, balance transfers or both. A break from finance A 0% APR credit card is a credit card that charges no interest on qualifying purchases, balance transfers or both for a fixed amount of time |  |
| Consider introductorh up automatic Identity theft protection to make sure you don't miss a petiods date, which could result in penalties that increase your balance. By federal low introductory APR periods, intro APR periods must last pediods least six months. Credit cards will often offer both to new cardholders. Annual percentage rate, or APR, refers to the interest rate a credit card company charges you to borrow money. If you are currently using a non-supported browser your experience may not be optimal, you may experience rendering issues, and you may be exposed to potential security risks. These cards can help you save money, consolidate debt and, in some cases, take advantage of nice perks and rewards. | Find the right credit card for you. There it is. Experian is a Program Manager, not a bank. However, if you have a balance when the introductory period ends, all of the interest that would have accrued during the promotional period will be added to your balance. Further, most issuers also won't allow you to transfer a balance from one of their cards to another. If your account has a balance remaining after the introductory period ends, you can either transfer your debt or work to pay off the debt with interest. | If you pay off your purchases in full before your 0 percent intro APR period expires, you won't pay interest on them at all. If you transfer a The introductory period begins as soon as the account is created. This means that if it comes with a 0 percent APR for 12 months and the credit APR: 0% intro APR for 21 months from account opening on purchases and qualifying balance transfers, and then the ongoing APR of %, % | Intro purchase APR: 0% intro APR for 18 billing cycles on Purchases, followed by a % - % (Variable) APR. Intro Balance Transfer APR0% If a card offers a 0% intro APR, this means you won't have to pay interest during the introductory period. And that could apply to qualifying purchases, balance The 0% intro APR is a promotional interest rate typically offered to new credit card customers. It can apply to regular purchases, balance transfers or both | A 0% APR on a credit card means that you won't be charged interest on purchases, balance transfers or both, for a fixed period of time An intro, or introductory 0% APR means there is a period of time after you open the account when the interest rate on transactions or balance Credit cards that offer a 0% intro APR can help you pay for big-ticket items like appliances, furniture, computers or airplane tickets |  |
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Unvergleichlich topic, mir gefällt))))