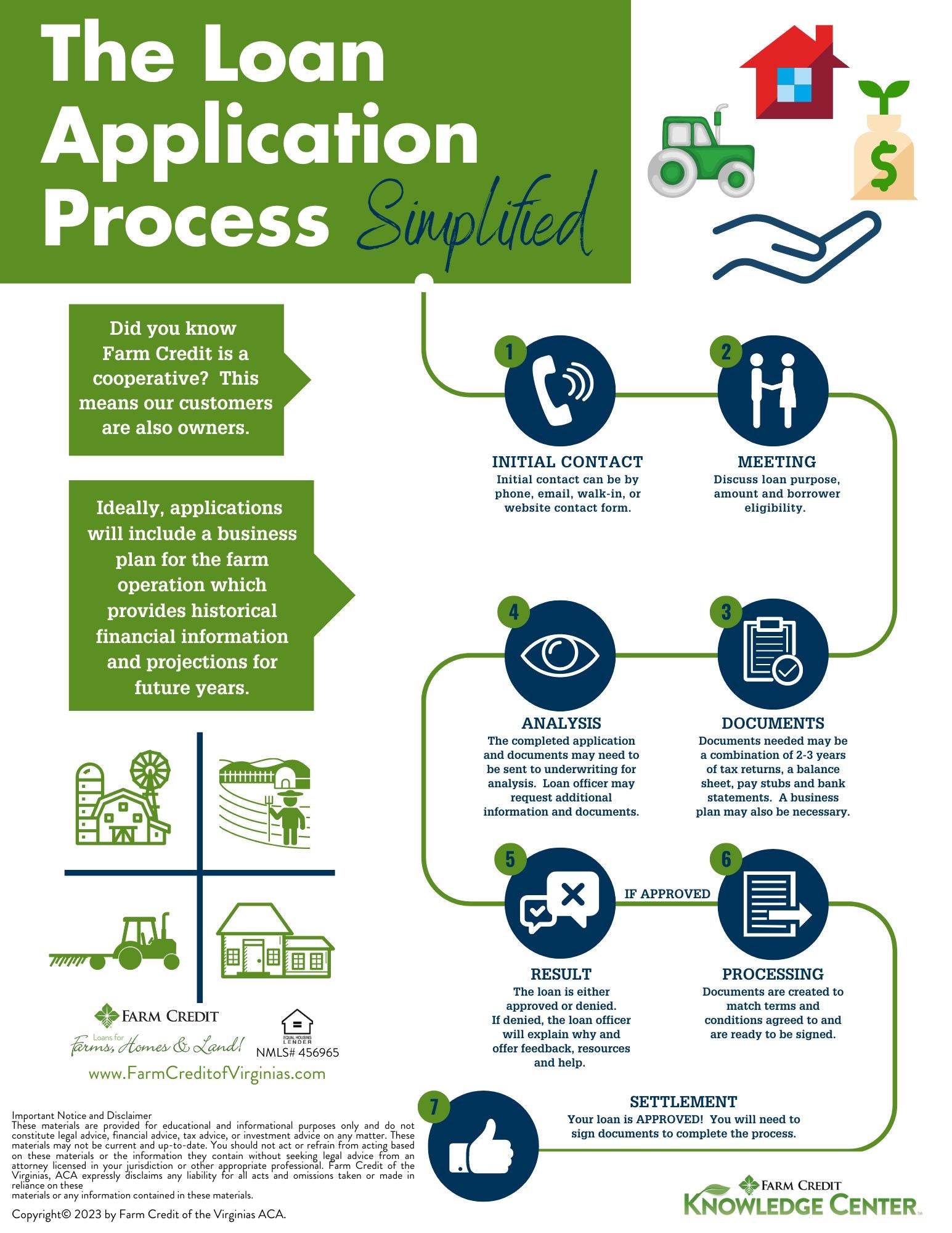
When assessing creditworthiness, both your personal and business finances matter. On the business side, a bank will determine if your business is generating a positive cash flow.
Before you approach a lender, request a copy of your personal credit report and your business credit report from the three credit reporting agencies Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion , and review them carefully for accuracy. If you spot an error, file an online dispute with the applicable agency within 30 days of receiving your report.
Providing comprehensive and accurate information can help your application move through the process as quickly as possible. Be prepared to tell the lender how you plan to use the money.
For example, you may explain that you will use the capital to pay for additional office space and furniture or for a website redesign. Also be sure you are asking for a realistic amount to fulfill those particular goals. The cost of materials have gone up quickly in recent years, so a remodeling project this year may be considerably costlier than the quote you got two years ago.
This information will help your financial professional determine whether your business is currently able to take on the debt required to fund such improvements.
You will also want to consider the process and the timing. Some things to keep in mind:. You also have to decide how long you will need to repay your credit. There are short-, medium-, and long-term loans, and they all have positives and negatives. For example, if you expect to be able to pay back the money quickly, a short-term loan may be the best choice.
Interest rates can also have a big impact on your decision. Bottom line: Just as planning and preparation can help you set the business goals that will help you succeed, planning and preparation can help you apply for and secure the funds needed to reach them.
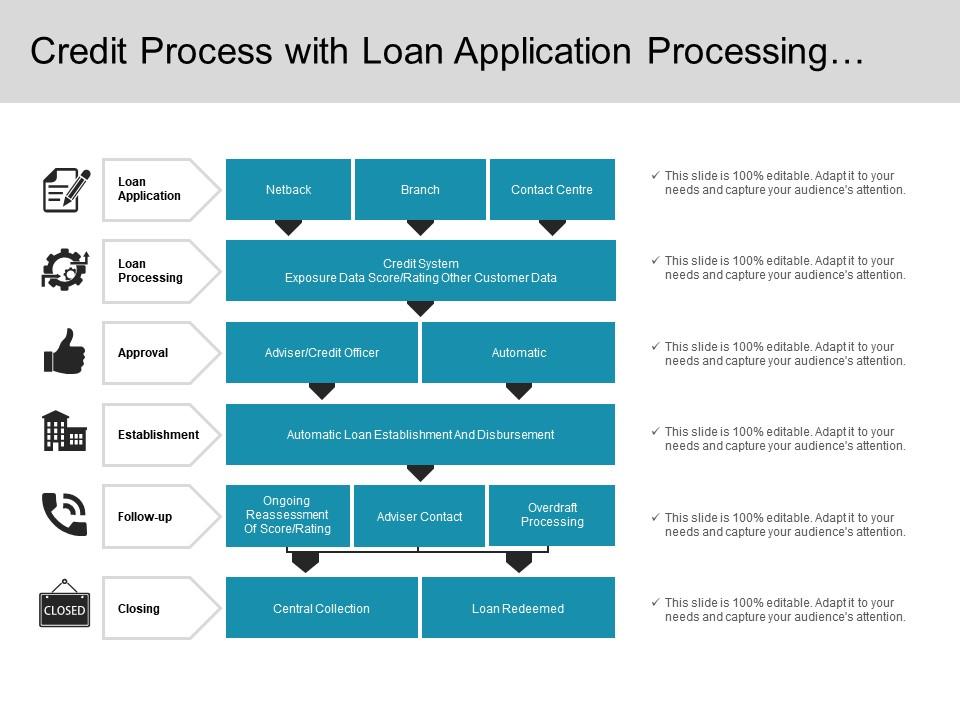
Resources tailored to the needs of women-led businesses, designed to help you succeed. Every bank has a team of commercial relationship managers who are supervised by a sales manager. He or she is usually the first person to view the loan request.
loan and deposit accounts, and is actively involved in enticing prospective borrowers and depositors to have a banking relationship with the bank. Credit officer: he or she is authorized by the bank to approve or deny a credit request by a prospective borrower.
The credit officer assesses a loan application to determine whether it is viable or not and assesses the financial history of the prospective borrower to gauge whether it is a risk worth taking or not.
Credit analyst: this person analyses the financial information and situation of the borrower, and analyses all the information accumulated by the relationship manager vis-à-vis the borrower i.
to evaluate the credit risk of the prospective borrowing company. He or she uses ratios — profitability ratios, leverage ratios , coverage credit analysis ratios, and liquidity ratios — to assist in the credit analysis process.
Following the aforesaid analysis, the same is included in a loan approval document. If the credit is approved, this document is signed by the relationship manager and the credit officer. Usually, loans made are term loans. Relationship and Sales — in the next step, the relationship manager forwards the loan request to the sales manager.
They discuss the profile of the prospective borrower and whether they wish to take the loan request forward or not. If the decision is to go ahead, then the sales manager will get back to the prospective borrower and request the audited financial statements of the company — balance sheet , income statement and cash flow statements , and any other documents that are required for the credit approval process.
Credit analysis: the aforesaid documents are then forwarded to the credit analyst of the bank. Then the relationship manager and the credit analyst discuss the proposed structure of the loan.
The point of structuring a loan is to mitigate risk. Following the discussions, the credit team performs a credit analysis of a company that wants to borrow.
This involves assessing business risk and financial risk. Upon completion of the analysis, a loan approval document is prepared, which is sometimes referred to as a credit memo. Loan approval document or credit memo: this document includes details such as the debt capacity of the borrower, clarity on risks involved and mitigating factors to those risks, a summary of the loan request that includes the loan amount, term of the loan, proposed interest rate, use of funds, and guarantors among other details, and information of the prospective borrowing company with reference to what it does, how long has it been in operation and its operating experience.
The loan approval document ie. The analysis of the ability of the company to repay the debt in full and on time is also included in this document. This assessment includes an analysis of past data, growth trends, overall industry trends, proposed loan terms, and making certain assumptions that will help the bank to estimate the debt service coverage ratio DSCR.
Next, insights pertaining to the financial statements are mentioned in this document and contain key ratios, historical trends, and some data that reflects the financial health of the company. Further, details about the guarantor of the loan, financial analysis of the same, the ability of the guarantor to cover any shortfalls in debt servicing, and liquidity of guarantor-related analysis are also stated in this document.
Lastly, the loan approval document contains information regarding whether the prospective borrower is an existing or new client. Further, what other loans do they have outstanding, and do they have deposits? Having stated the above, once the loan approval document is completed by the credit analyst, it is forwarded to the relationship manager for examining the same.
There are usually two or three rounds of edits that take place and included proposed loan covenants too. After the contents of the loan approval document or credit memo are reviewed by the relationship manager and he or she is satisfied with it, it will be reviewed by the credit officer.
Once this is ensured, thereafter, the credit officer will sign this document with the relationship manager. Upon approval of the credit request by the credit officer, the relationship manager gets in touch with the prospective borrower and outlines the approved structure of the loan.
This is sent in a term sheet. The borrower could try to alter some aspects of the deal but usually does not have too much latitude. If the terms of the loan are acceptable, the borrower signs the term sheet. Three factors should be taken into account vis-à-vis the segmentation of the credit approval process i.
structuring such a process. Type of borrower: in general, is used as the highest layer in the process of credit approval. The type of borrowers can be categorized into sovereign borrowers, other public authorities, corporates, and individual borrowers i.
the retail segment. Each of them has a different risk profile. Cash flows source: the credit review has to focus on the asset that has to be financed and the cash flows that are expected from the same.
Value and type of collateral: the value and type of collateral have a major impact on the risk associated with lending. Some types of forms of lending give the lender a substantial degree of control over the asset being financed and consequently lower their risk exposure — when compared to other types of collateralized lending.
For example, mortgage finance and leasing finance. Consequently, if there is a rise in the level of exposure to a prospective borrower, it should trigger a more comprehensive credit approval review for the purpose of risk minimization.
From a risk perspective, the quality of the credit approval process is determined by the best possible identification and assessment of the credit risk resulting from a loan request.
The credit risk can be categorized or distributed into three risk components.
A credit application is a form a borrower fills out to request credit. The form can usually be submitted either online or in person. Key A credit application is a document that an individual or a business completes when they are seeking to establish a credit relationship with a lender The credit application process is the credit professional's first, and sometimes only, opportunity to protect their company from risk of loss through credit
Wacker, dieser sehr gute Gedanke fällt gerade übrigens
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Es ist Gelöscht (hat topic) verwirrt
Es wird der letzte Tropfen.
die Prächtige Idee und ist termingemäß