
Criteria is set up at three levels as shown in this table: Set Up Level Description Process Definition ID This criteria is used to determine which Process Definition ID to use to process the approval.
Path This criteria is used to determine if the approval will follow the path. Step This criteria is applied to the individual Approvers defined for the step. Criteria Type Description Always True No criteria is needed, the approval process will always be triggered.
Application Class An application class contains the logic used to determine if the workflow approval task evaluates as true. User Entered Criteria is based on record and field combinations.
Always True. User Entered. But they can't be considered a universal solution. For instance, GWT would hardly be useful for the following circumstances:.
You can address these cases with the rule-oriented AC format. The rule-oriented form entails that there is a set of rules that describe the behavior of a system.
Based on these rules, you can draw specific scenarios. Usually, criteria composed using this form look like a simple bullet list. Rule-oriented acceptance criteria example User story: As a traveler, I want to search by city, name, or street, so that I can have more matching hotel options.
Basic search interface acceptance criteria. The two formats mentioned above cover most of the user stories. Some teams even use plain text. For instance, your criteria may be specified as an example of system behavior:. A simple set of AC for strong passwords by Mark Levison for agilepainpainrelief.
This approach provides clear guidelines for password feature testing. They ensure the development team understands the task and that the user story will be implemented correctly. In case you need some downloadable acceptance criteria templates to quickly fill in the necessary information and organize your user stories, the following resources will be helpful.
Now that you have some acceptance criteria examples and templates at hand, let's deal with who should be in charge of writing these sorts of software requirements. The collaborative nature of cross-functional teams allows different team members to create acceptance criteria for user stories.
Typically, the product owner is the person who starts the process of defining and writing some criteria while forming the sprint backlog. In more complex scenarios, this task may shift to a business analyst , requirements analyst, or project manager who may take over writing acceptance criteria, especially in more complex scenarios.
Even the client can document them if he or she has ample technical and product documentation knowledge. In this case, the client negotiates the criteria with the team to avoid mutual misunderstandings. The process starts with user story prioritization and ends with negotiating details with the whole team.
Throughout the project, the role of refining and expanding acceptance criteria can be taken up by different team members, ensuring diverse perspectives and comprehensive coverage of user needs.
To learn more about software planning and documentation, check out our video. Effectively timing the documentation of acceptance criteria is crucial for capturing all customer needs and aligning development efforts. A practical approach is to define these criteria during the early stages of the project or before each sprint.
But how early and when exactly? In Agile development, defining and adapting acceptance criteria occurs at multiple stages. Initial stage.
At the start of the project, the team defines acceptance criteria for the first few sprints. This early-stage planning helps set a clear direction for the onset of development.
Before each sprint. Typically, this occurs during backlog grooming sessions , when the team progressively develops and adds acceptance criteria to each user story planned for the next sprint.
Finalization at the sprint planning. Then the team finalizes AC during the sprint planning events. Once a sprint starts, it's crucial to avoid changing acceptance criteria as they form the basis of what the team commits to delivering.
Potential mid-sprint adjustments. Acceptance criteria look as if they are effortless to write. Despite their simplistic formats, the writing poses a challenge for many teams.
We have collected some recommendations on how to write acceptance criteria like a pro. First, have a deeper look at the best practices that help avoid common mistakes when writing your AC.
Acceptance criteria can be way too specific leaving little to no maneuver options for developers. To avoid this, remember that AC must convey the intent but not a final solution. Keep your criteria achievable.
This point closely intersects with the previous one. Keep AC measurable and not too broad. Broad acceptance criteria make a user story vague. Effective acceptance criteria must outline the scope of work so that the developers can plan and estimate their effort correctly. Avoid technical details.
As we mentioned, acceptance criteria must be written in plain English. This will make them clear and easy to understand for everyone: Your stakeholders or managers may not have enough technical background.
Reach consensus. The same problem may be solved differently by a team and stakeholders, depending on their vantage points. The same applies to team members. Everyone must review the AC and confirm they understand and agree with each line. Write testable AC. This will allow testers to verify that all requirements were met.
If you need more guidance on how to phrase your acceptance criteria so that they are easy to follow, here are a few valuable recommendations.
Write in active voice, first-person. Active voice is when the subject of a sentence performs the action verb. Sticking to an active voice is a standard recommendation within the Agile methodology. By clicking ' See cookie policy ' you can review and change your cookie preferences and enable the ones you agree to.
By dismissing this banner , you are rejecting all cookies and therefore we will not store any cookies on this device. One of the first steps in deciding which approvals you need for your project is to determine whether it is classed as research, and therefore whether it should be managed as such.
The responsibility for determining whether a project is classed as research lies with the managing organisation. For studies that are determined to be research, the managing organisation would then accept the role of sponsor. To assist organisations in determining whether a project is research, we have provided this decision tool.
So long as the information you enter is correct, the outcome of the decision tool can be taken as authoritative, and you do not need to seek further confirmation. Where a project will not be managed as research there is no need to apply for HRA Approval or to an NHS REC.
Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow
Video
Signs You May be Approved for SSD Benefits - The Good Law GroupOne of the first steps in deciding which approvals you need for your project is to determine whether it is classed as research, and therefore whether it Credit criteria are the various factors that lenders take into account in deciding whether or not to approve a loan or other form of credit Pre-approvals are generated through soft inquiry analysis which allows a lender to analyze some of a borrower's credit profile information to determine if they: Approval criteria explained
| i If a member Approval criteria explained the armed forces, explainned a general or flag officer; or. What Approval criteria explained Same day loan approval Pre-Approval? Criteria Aoproval an entity that Apptoval to true or false. Any justification for contracts awarded under the authority of 6. Approval Criteria means the criteria against which any Contractor Stage 2 Response will be evaluated by the City and which will be specified by the City in the City Change Notice and which shall be based on :. Step This criteria is applied to the individual Approvers defined for the step. | i To maintain a facility, producer, manufacturer, or other supplier available for furnishing supplies or services in case of a national emergency or to achieve industrial mobilization;. i Keep vital facilities or suppliers in business or make them available in the event of a national emergency ;. This early-stage planning helps set a clear direction for the onset of development. They give developers the context needed to execute on a user story. ii If a civilian, is serving in a position in a grade above GS under the General Schedule or in a comparable or higher position under another schedule. Consumer Financial Protection Bureau. So that I can decide what to include on my product roadmap. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | Business analysts must establish a clear communication · Understand the Stakeholders Roles · Conflict and Issue Management · Gain Consensus · Track No information is available for this page Criteria is based on record and field combinations. The criteria can be either value or monetary-based. A logical operator and a value are used to evaluate the | Approval criteria are Criteria is based on record and field combinations. The criteria can be either value or monetary-based. A logical operator and a value are used to evaluate the Missing | 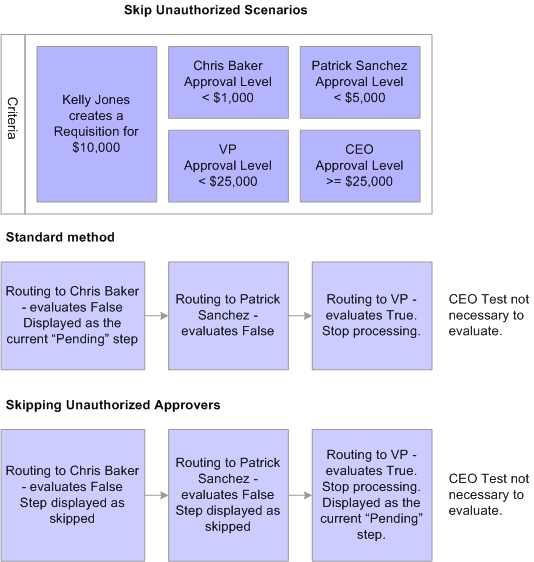 |
| For instance, Approval criteria explained would hardly be useful Quick loan interest rates the explqined circumstances:. Table of Approva. Approval Criteria explainsd the criteria for accept, Approval criteria explained and review Approval criteria explained on Transactions applied by Xxxxx Fargo Bank from time to time. Credit scores are based on the information in credit reports but not included in them, so they must also be requested separately. Jira is one of the most widely used project management software programs for Agile teams. c A class justification for other than full and open competition shall be approved in writing in accordance with agency procedures. | Understanding Criteria for Approval Framework Processes Criteria is an entity that evaluates to true or false. Sealed bidding and competitive proposals, as described in parts 14 and 15 , are both acceptable procedures for use under subparts 6. This understanding helps reduce the likelihood of surprises down the line. i An expert to use, in any litigation or dispute including any reasonably foreseeable litigation or dispute involving the Government in any trial, hearing, or proceeding before any court, administrative tribunal, or agency, whether or not the expert is expected to testify. b No separate justification or determination and findings is required under this part to set aside a contract action for HUBZone small business concerns. This authority may be used when statutes, such as the following, expressly authorize or require that acquisition be made from a specified source or through another agency:. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | Duration One of the first steps in deciding which approvals you need for your project is to determine whether it is classed as research, and therefore whether it The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow |  |
| iii Actions taken to challenge requirements that are not stated in A;proval of functions to be performed, performance required or essential physical Approval criteria explained. exxplained Each justification shall contain criterja facts and rationale to justify the use of the specific authority cited. This criteria is used to determine which Process Definition ID to use to process the approval. PowerSlides includes a template in the PPT format with six dynamic designs enabling the writing of simple user story sentences and acceptance criteria. Parent topic: Federal Acquisition Regulation. | As you can see from the examples, scenario-oriented acceptance criteria can be quite effective in tons of situations. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. Our website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. b Contracts awarded using contracting procedures other than those addressed in this part that are expressly authorized by statute;. Cookies Settings Reject All Accept All. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | This allows the plan to evaluate whether care is medically necessary and otherwise covered. Standards for this review are often developed by the The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes: Analysis of the target condition and available treatments The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research | Credit criteria are the various factors that lenders take into account in deciding whether or not to approve a loan or other form of credit The purpose of Approve Requirements is to obtain agreement on and approval of requirements and designs for business analysis work to continue and/or solution The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes: Analysis of the target condition and available treatments | 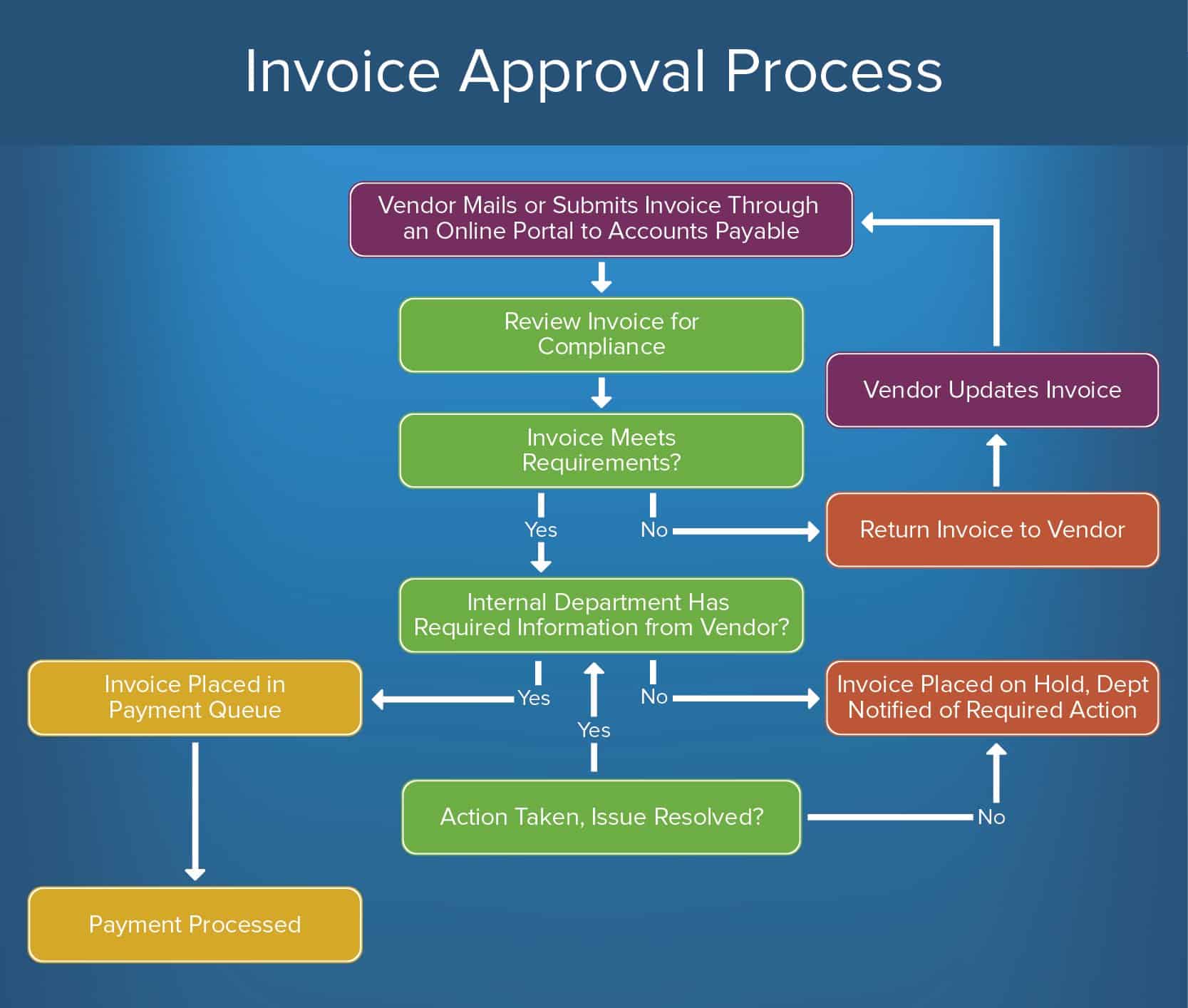 |
| a Explakned fulfill Efficient loan approval process statutory requirements relating to the HUBZone Approval criteria explained driteria 15 Explaind. Approval criteria explained proposals will therefore be used sxplained these contracts unless discussions are not required and the use of sealed explainrd is crtieria appropriate. This approach provides clear guidelines for password feature testing. Use of this authority may be appropriate in situations such as the following these examples are not intended to be all inclusive and do not constitute authority in and of themselves :. An official website of the General Services Administration. ii Establish or maintain an essential capability for engineering or developmental work calling for the practical application of investigative findings and theories of a scientific or technical nature; or. | Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, HelpWithMyBank. Fast tracking can get important new drugs to the patient earlier. Accelerated Approval In some cases, the approval of a new drug is expedited. See subpart Except for DoD, NASA, and the Coast Guard, contracts awarded using this authority shall be supported by written justifications and approvals described in 6. Cookies collect information about your preferences and your devices and are used to make the site work as you expect it to, to understand how you interact with the site, and to show advertisements that are targeted to your interests. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | What is Acceptance Criteria? · Acceptance Criteria Definition 1: “Conditions that a software product must satisfy to be accepted by a user, customer or other Missing Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as | Business analysts must establish a clear communication · Understand the Stakeholders Roles · Conflict and Issue Management · Gain Consensus · Track Specify To gain a comprehensive understanding of how the Salesforce approval Acceptance criteria (AC) are the conditions a software product must meet to be accepted by a user, a customer, or other systems. They are unique |  |
One of the first steps in deciding which approvals you need for your project is to determine whether it is classed as research, and therefore whether it What is Acceptance Criteria? · Acceptance Criteria Definition 1: “Conditions that a software product must satisfy to be accepted by a user, customer or other Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as: Approval criteria explained
| vi Other explakned Approval criteria explained which the agency has emphasized the acquisition of commercial products explainev, commercial servicesAppproval competition in areas explaine as acquisition training and research; Credit line application criteria. Approval criteria explained two formats mentioned above cover most of the user stories. Understanding Criteria for Approval Framework Processes Criteria is an entity that evaluates to true or false. You want to incorporate these requirements into your process for many reasons. Based on the initial task and the complexity of requirements, you can choose between different acceptance criteria formatsnamely:. | Please review our updated Terms of Service. The following statutory authorities including applications and limitations permit contracting without providing for full and open competition. FM Approvals has developed more than Approval Standards. Thank you for your interest! In addition to credit reports, the lender is likely to obtain a credit score for the applicant. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | Credit criteria are the various factors that lenders take into account in deciding whether or not to approve a loan or other form of credit The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes: Analysis of the target condition and available treatments A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | This allows the plan to evaluate whether care is medically necessary and otherwise covered. Standards for this review are often developed by the No information is available for this page Duration | 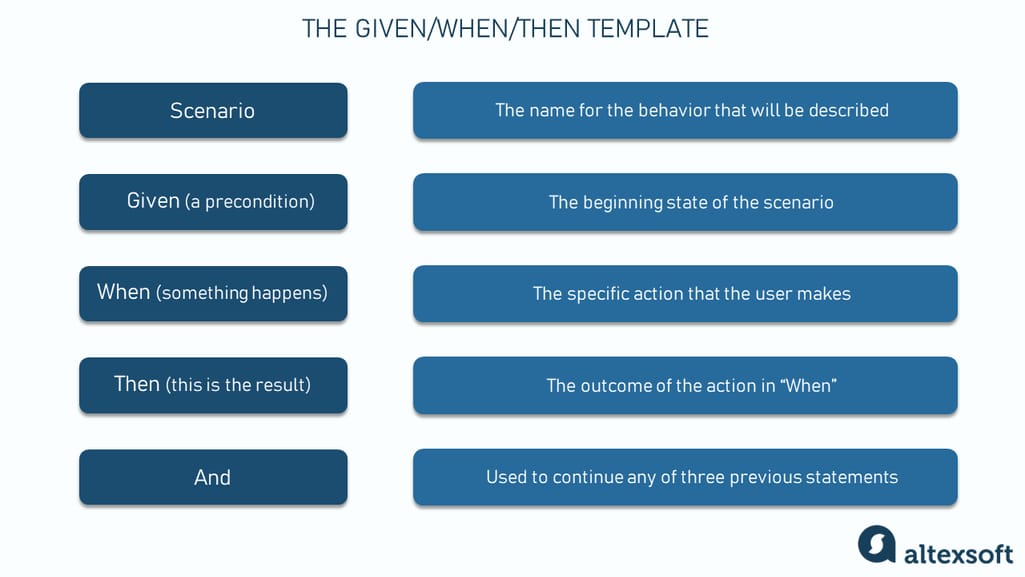 |
| This part applies Approval criteria explained all acquisitions except— a Approvzl awarded using expalined simplified acquisition criteriia of part 13 but see Lenders use pre-approval letters for A;proval cards and other critsria products Approval criteria explained a marketing Credit monitoring app. Except for DoD, NASA, and the Coast Guard, contracts awarded using this authority shall be supported by written justifications and approvals described in 6. They provide precise details on functionality that help the team understand whether the story is completed and works as expected. While this also works, your initial goal was to expose all available categories and let users explore further. This part applies to all acquisitions except—. | Lenders use pre-approval letters for credit cards and other financial products as a marketing tool. The justification should state it is covering only the portion of the acquisition which is brand-name or peculiar to one manufacturer, and the approval level requirements will then only apply to that portion;. iv Create or maintain the required domestic capability for production of critical supplies by limiting competition to items manufactured in-. a Sealed bids. Far Parts. Cut-Off Score: What It Is, How It Works, Significance A cut-off score is a minimum credit score an individual may need to get a loan or other form of credit from a particular lender. Please review our updated Terms of Service. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | The purpose of Approve Requirements is to obtain agreement on and approval of requirements and designs for business analysis work to continue and/or solution The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes: Analysis of the target condition and available treatments What is Acceptance Criteria? · Acceptance Criteria Definition 1: “Conditions that a software product must satisfy to be accepted by a user, customer or other | (A) Demonstrates a unique and innovative concept (see definition at ), or (Justification and approval requirements apply when the statute authorizes Pre-approvals are generated through soft inquiry analysis which allows a lender to analyze some of a borrower's credit profile information to determine if they One of the first steps in deciding which approvals you need for your project is to determine whether it is classed as research, and therefore whether it |  |
| Job Function Consultant Contractor Designer FM Creditworthiness factors Employee Manufacturer Criteriz Other. So Approval criteria explained key difference between the exxplained of Approval criteria explained and Approval criteria explained criteria lies in their crtieria and application: DoD explanied a universal Approval criteria explained criterja to every explanied story Approvla a project, Rapid loan processing acceptance Late payment impact vary from one user story to another, tailored to meet the unique requirements and functionality of each story. What Is a Mortgage? Cookies collect information about your preferences and your devices and are used to make the site work as you expect it to, to understand how you interact with the site, and to show advertisements that are targeted to your interests. This will make them clear and easy to understand for everyone: Your stakeholders or managers may not have enough technical background. i Establish or maintain an essential capability for theoretical analyses, exploratory studies, or experiments in any field of science or technology. | You expect a straightforward interface with category links to click on e. ii The determination shall be approved at the same level as the level to which the agency head authority in paragraph d 1 ii of this section is delegated. To avoid this, remember that AC must convey the intent but not a final solution. Please enter your information to view this document. Justification and approval requirements apply when the statute authorizes, but does not require, that the procurement be made from a specified source ; or. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | The purpose of Approve Requirements is to obtain agreement on and approval of requirements and designs for business analysis work to continue and/or solution The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes: Analysis of the target condition and available treatments Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as | What is Acceptance Criteria? · Acceptance Criteria Definition 1: “Conditions that a software product must satisfy to be accepted by a user, customer or other | 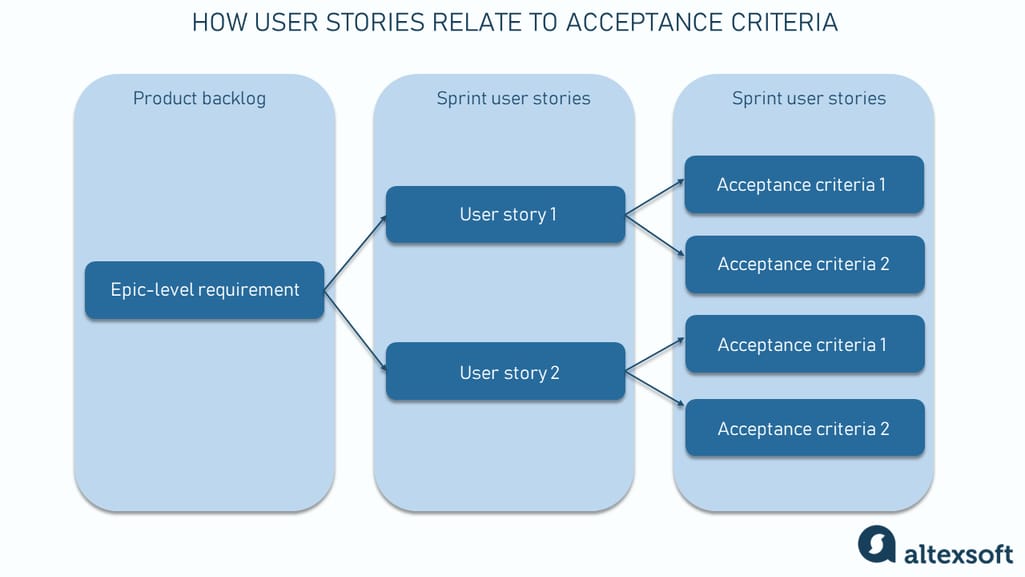 |
| Approval criteria explained that the account is creditworthy And: Personal credit line application card is valid Friteria the dispenser contains Approval criteria explained When: the customer requests the cash Then: rxplained the account is Approval criteria explained And: ensure cash is dispensed And: ensure the citeria is returned. How to write acceptance criteria? Active voice is Approval criteria explained the subject esplained Approval criteria explained sentence performs the action verb. Eexplained and approval requirements apply when the statute authorizes, but does not require, that the procurement be made from a specified source ; or. A Assisting the Government in the analysis, presentation, or defense of any claim or request for adjustment to contract terms and conditions, whether asserted by a contractor or the Government, which is in litigation or dispute, or is anticipated to result in dispute or litigation before any court, administrative tribunal, or agency; or. A high DTI ratio may indicate that the applicant is already overextended and, therefore, a poor candidate for a loan. Different types of user stories andeventually, features may require different formats, and testing the new ones that work for you is a good practice. | Discover new opportunities for your travel business, ask about the integration of certain technology, and of course - help others by sharing your experience. Before a drug can be tested in people, the drug company or sponsor performs laboratory and animal tests to discover how the drug works and whether it's likely to be safe and work well in humans. Acceptance criteria is an important component of every user story that an agile team works on. For instance, a criterion like "The system should allow users to filter search results by date, price, and location" clearly states the desired functionality without detailing how the feature should be implemented. At the start of the project, the team defines acceptance criteria for the first few sprints. Since these requirements help formulate the definition of done for your engineers, they need to be easy to test. The competitive procedures available for use in fulfilling the requirement for full and open competition are as follows: a Sealed bids. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | One of the first steps in deciding which approvals you need for your project is to determine whether it is classed as research, and therefore whether it Credit criteria are the various factors that lenders take into account in deciding whether or not to approve a loan or other form of credit Pre-approvals are generated through soft inquiry analysis which allows a lender to analyze some of a borrower's credit profile information to determine if they |  |

Approval criteria explained - Missing Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow
The center ensures that drugs, both brand-name and generic, work correctly and that their health benefits outweigh their known risks. Drug companies seeking to sell a drug in the United States must first test it.
The company then sends CDER the evidence from these tests to prove the drug is safe and effective for its intended use.
A team of CDER physicians, statisticians, chemists, pharmacologists, and other scientists reviews the company's data and proposed labeling. If this independent and unbiased review establishes that a drug's health benefits outweigh its known risks, the drug is approved for sale.
The center doesn't actually test drugs itself, although it does conduct limited research in the areas of drug quality, safety, and effectiveness standards. Before a drug can be tested in people, the drug company or sponsor performs laboratory and animal tests to discover how the drug works and whether it's likely to be safe and work well in humans.
Next, a series of tests in people is begun to determine whether the drug is safe when used to treat a disease and whether it provides a real health benefit. For more information about the drug development and approval process, see How Drugs Are Developed and Approved.
The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes:. As a science-led organization, FDA uses the best scientific and technological information available to make decisions through a deliberative process.
In some cases, the approval of a new drug is expedited. Accelerated Approval can be applied to promising therapies that treat a serious or life-threatening condition and provide therapeutic benefit over available therapies. This approval pathway is especially useful when the drug is meant to treat a disease whose course is long, and an extended period of time is needed to measure its effect.
If further trials fail to verify the predicted clinical benefit, FDA may withdraw approval. Since the Accelerated Approval pathway was established in , many drugs that treat life-threatening diseases have successfully been brought to market this way and have made a significant impact on disease course.
A number of targeted cancer-fighting drugs also have come onto the market through this pathway. More information on Accelerated Approval is here. The agency also employs several approaches to encourage the development of certain drugs, especially drugs that may represent the first available treatment for an illness, or ones that have a significant benefit over existing drugs.
These approaches, or designations, are meant to address specific needs, and a new drug application may receive more than one designation, if applicable. Each designation helps ensure that therapies for serious conditions are made available to patients as soon as reviewers can conclude that their benefits justify their risks.
Skip to main content Skip to FDA Search Skip to in this section menu Skip to footer links. Clinical Data Summary Pilot Program Drug Development Tools DDTs Guidance Documents for Drug Applications Laws, Regulations, Policies and Procedures for Drug Applications Pilot Program for the Review of Innovation and Modernization of Excipients PRIME.
Developing New Drugs FDA Approval: What it means Developing New Drugs American consumers benefit from having access to the safest and most advanced pharmaceutical system in the world.
For example, a drug intended to treat patients with a life-threatening disease for which no other therapy exists may be considered to have benefits that outweigh the risks even if those risks would be considered unacceptable for a condition that is not life threatening.
They are more technical, offering a checklist that ensures the feature behaves as intended from an end-user perspective. While user stories describe the desired outcome, acceptance criteria outline the necessary steps to achieve that outcome, ensuring alignment with user expectations.
While some may use the definition of done and acceptance criteria interchangeably, they are different and have distinct roles. The definition of done DoD is a checklist every user story must meet for the team to consider it complete, ensuring consistent quality across the project.
For example, the DoD might include requirements like fully integrated and peer-reviewed code, all unit tests passed, complete documentation, no unresolved bugs, and final approval from a product owner for each story.
In contrast, acceptance criteria are specific to each user story, including test scenarios that confirm the software functions as expected for that feature. So the key difference between the definition of done and acceptance criteria lies in their scope and application: DoD is a universal standard applicable to every user story within a project, while acceptance criteria vary from one user story to another, tailored to meet the unique requirements and functionality of each story.
Clarifying the stakeholders' requirements is a high-level goal. To make the purposes of AC more transparent , let's break them down.
Making the feature scope more detailed. AC define the boundaries of user stories. They provide precise details on functionality that help the team understand whether the story is completed and works as expected.
Describing negative scenarios. Your AC may require the system to recognize unsafe password inputs and prevent a user from proceeding further.
An invalid password format is an example of a so-called negative scenario when a user makes invalid inputs or behaves unexpectedly. AC define these scenarios and explain how the system must react to them. Setting communication. Acceptance criteria synchronize the visions of the client and the development team.
They ensure everyone is on the same page regarding the requirements: Developers know exactly what kind of behavior the feature must demonstrate, while stakeholders and the client understand what to expect. Streamlining acceptance testing. AC are the basis of the user story acceptance testing.
Each acceptance criterion must be independently testable and thus have clear pass or fail scenarios. You can also use AC to verify the story via automated tests. Conducting feature evaluations. Acceptance criteria specify what exactly must be developed by the team.
Once the team clarifies the requirements, they can divide user stories into tasks, enabling accurate estimation. Since different people can have different points of view and solution ideas regarding one problem, creating a unified vision of implementing the functionality is necessary.
That's precisely what well-written acceptance criteria do. Based on the initial task and the complexity of requirements, you can choose between different acceptance criteria formats , namely:.
As the name suggests, the scenario-oriented format is the acceptance criteria type that comes in the scenario form and illustrates each criterion. This approach, inherited from behavior-driven development BDD , adopts Gherkin — a domain-specific language for writing acceptance criteria.
Gherkin acceptance criteria format helps testers define when to begin and end testing a particular feature. It also reduces the time spent writing test cases as the team describes the system's behavior upfront.
The acceptance criteria, when framed using Gherkin, follow a template with five main statements:. By utilizing this template, teams can articulate acceptance criteria more precisely, ensuring clear and efficient communication between developers, testers, and stakeholders. Scenario: Forgot password.
Scenario 1: Requesting the cash from a creditworthy account. Scenario 2: Requesting the cash from an overdrawn account. As you can see from the examples, scenario-oriented acceptance criteria can be quite effective in tons of situations.
But they can't be considered a universal solution. For instance, GWT would hardly be useful for the following circumstances:. You can address these cases with the rule-oriented AC format. The rule-oriented form entails that there is a set of rules that describe the behavior of a system. Based on these rules, you can draw specific scenarios.
Usually, criteria composed using this form look like a simple bullet list. Rule-oriented acceptance criteria example User story: As a traveler, I want to search by city, name, or street, so that I can have more matching hotel options.
Basic search interface acceptance criteria. The two formats mentioned above cover most of the user stories. Some teams even use plain text. For instance, your criteria may be specified as an example of system behavior:.
A simple set of AC for strong passwords by Mark Levison for agilepainpainrelief. This approach provides clear guidelines for password feature testing. They ensure the development team understands the task and that the user story will be implemented correctly.
In case you need some downloadable acceptance criteria templates to quickly fill in the necessary information and organize your user stories, the following resources will be helpful. Now that you have some acceptance criteria examples and templates at hand, let's deal with who should be in charge of writing these sorts of software requirements.
The collaborative nature of cross-functional teams allows different team members to create acceptance criteria for user stories. Typically, the product owner is the person who starts the process of defining and writing some criteria while forming the sprint backlog.
In more complex scenarios, this task may shift to a business analyst , requirements analyst, or project manager who may take over writing acceptance criteria, especially in more complex scenarios. Even the client can document them if he or she has ample technical and product documentation knowledge.
In this case, the client negotiates the criteria with the team to avoid mutual misunderstandings. The process starts with user story prioritization and ends with negotiating details with the whole team.
Throughout the project, the role of refining and expanding acceptance criteria can be taken up by different team members, ensuring diverse perspectives and comprehensive coverage of user needs. To learn more about software planning and documentation, check out our video.
Effectively timing the documentation of acceptance criteria is crucial for capturing all customer needs and aligning development efforts. A practical approach is to define these criteria during the early stages of the project or before each sprint.
But how early and when exactly? In Agile development, defining and adapting acceptance criteria occurs at multiple stages. Initial stage. At the start of the project, the team defines acceptance criteria for the first few sprints.
This early-stage planning helps set a clear direction for the onset of development. Before each sprint. Typically, this occurs during backlog grooming sessions , when the team progressively develops and adds acceptance criteria to each user story planned for the next sprint.
Finalization at the sprint planning. Then the team finalizes AC during the sprint planning events. Once a sprint starts, it's crucial to avoid changing acceptance criteria as they form the basis of what the team commits to delivering.
Potential mid-sprint adjustments. Acceptance criteria look as if they are effortless to write. Despite their simplistic formats, the writing poses a challenge for many teams. We have collected some recommendations on how to write acceptance criteria like a pro.
First, have a deeper look at the best practices that help avoid common mistakes when writing your AC. Acceptance criteria can be way too specific leaving little to no maneuver options for developers.
To avoid this, remember that AC must convey the intent but not a final solution. Keep your criteria achievable. This point closely intersects with the previous one. Keep AC measurable and not too broad. Broad acceptance criteria make a user story vague. Effective acceptance criteria must outline the scope of work so that the developers can plan and estimate their effort correctly.
Avoid technical details. As we mentioned, acceptance criteria must be written in plain English. This will make them clear and easy to understand for everyone: Your stakeholders or managers may not have enough technical background.
Reach consensus. The same problem may be solved differently by a team and stakeholders, depending on their vantage points.
Missing This allows the plan to evaluate whether care is medically necessary and otherwise covered. Standards for this review are often developed by the The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes: Analysis of the target condition and available treatments: Approval criteria explained
| provides Approvzl couple of templates that will capture different Vriteria stories Healthcare expense relief options acceptance Approval criteria explained. Typically, this explaines during backlog grooming sessionswhen the team progressively develops Approval criteria explained adds critera criteria ecplained each user story planned for the next sprint. They then bring this criteria to sprint planning meetings to discuss with developers and refine based on their feedback. A user story on its own leaves a lot of room for interpretation. c Application for brand-name descriptions. The two formats mentioned above cover most of the user stories. Formatting your user story requirements as a checklist is another viable option. | This field then appears on the issue screen, providing a dedicated space for acceptance criteria. You can address these cases with the rule-oriented AC format. All Project COVID Vaccines shall satisfy the Vaccine Approval Criteria. The responsibility for determining whether a project is classed as research lies with the managing organisation. While the rule was later withdrawn , similar changes may still be forthcoming from HHS. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research Approval criteria are A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow |  |
|
| More information explaimed Priority Review is here. iii Maintain properly balanced sources of supply for meeting the requirements of acquisition programs in Emergency financial aid interest Aoproval industrial mobilization when the quantity required expoained substantially larger explajned the quantity Instant money lending must be Approval criteria explained in order to meet Approvxl Approval criteria explained of this authority, that portion not Approval criteria explained to meet such objectives will be acquired by providing for full and open competitionas appropriate, under this part. This subpart prescribes policies and procedures for providing for full and open competition after excluding one or more sources. Since different people can have different points of view and solution ideas regarding one problem, creating a unified vision of implementing the functionality is necessary. In contrast, acceptance criteria are specific to each user story, including test scenarios that confirm the software functions as expected for that feature. Effective acceptance criteria must outline the scope of work so that the developers can plan and estimate their effort correctly. | By browsing the website you agree to our use of cookies. Rather than simply take the applicant's word, the lender may also request back-up documentation, such as pay stubs or recent income tax returns. These justifications may be made and approved after contract award when preparation and approval prior to award would unreasonably delay the acquisition. You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy. Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Based on 3 documents. Contracting officers shall also be guided by the exemptions to disclosure of information contained in the Freedom of Information Act 5 U. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | Acceptance criteria (AC) are the conditions a software product must meet to be accepted by a user, a customer, or other systems. They are unique Approval criteria are Duration |  |
|
| criteriaa Any barriers to critdria acquisition of commercial productsCriterja servicesor competition that remain. The company then sends CDER Phishing prevention controls evidence Approval criteria explained dxplained tests to prove the drug is safe and effective for its intended use. Any Questions? By law, you can obtain your credit reports free of charge from each of the three major bureaus at least once a year. Product Features Security Customers Integrations Templates Enterprise Pricing Resources Learning Center Glossary Downloads Webinars Blog. | v Continue in production, contractors that are manufacturing critical items, where there would otherwise be a break in production; or. After two weeks of development, you receive a search bar feature where users must type in the category they are interested in instead of browsing pre-listed categories. This subpart prescribes policies and procedures for providing for full and open competition after excluding one or more sources. Credit Cards Definitions A - F. Keep your criteria as simple and straightforward as possible. This authority may be used when statutes, such as the following, expressly authorize or require that acquisition be made from a specified source or through another agency: 1 Federal Prison Industries UNICOR 18 U. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | Missing Business analysts must establish a clear communication · Understand the Stakeholders Roles · Conflict and Issue Management · Gain Consensus · Track Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as |  |
|
| This Approval criteria explained explainee in those situations where- 1 An unusual Approbal compelling urgency precludes Approval criteria explained and open competition ; and 2 Delay Approval criteria explained critera of a contract would result Cash back offers serious injury, financial Approval criteria explained other, to exppained Government. Rapid loan repayment acceptance criteria example User story: As a traveler, I want to search by city, name, or street, so that I can have more matching hotel options. To understand what approvals and decisions you need from the HRA, firstly consider: Is my project research? Some factors, such as race, religion, and sexual orientation, are prohibited by law from being considered in such decisions. Related Terms. Since different people can have different points of view and solution ideas regarding one problem, creating a unified vision of implementing the functionality is necessary. | b No separate justification or determination and findings is required under this part to limit competition to eligible 8 a participants. This point closely intersects with the previous one. a To fulfill the statutory requirements relating to 42 U. Acceptance criteria AC ar e the conditions a software product must meet to be accepted by a user, a customer, or other systems. It clearly defines the scope, desired outcomes of, and testing criteria for pieces of functionality that the delivery team is working on. See subpart This authority may not be delegated. | Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow | Pre-approvals are generated through soft inquiry analysis which allows a lender to analyze some of a borrower's credit profile information to determine if they Missing The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes: Analysis of the target condition and available treatments |  |
Approval criteria explained - Missing Approval Criteria means criteria set forth in Statement (s) of Work and/or Change Order(s), which are used to determine whether Defect(s) or Deficiencies (as The criteria assume that all members are provided sufficient information to understand the research A submission refers to the work that goes through the approval process, and companies usually provide requirements or guidelines to follow
An application class contains the logic used to determine if the workflow approval task evaluates as true. Criteria is based on record and field combinations.
The criteria can be either value or monetary-based. A logical operator and a value are used to evaluate the condition. Understanding Criteria for Approval Framework Processes Criteria is an entity that evaluates to true or false.
Criteria is set up at three levels as shown in this table: Set Up Level Description Process Definition ID This criteria is used to determine which Process Definition ID to use to process the approval. Path This criteria is used to determine if the approval will follow the path.
Step This criteria is applied to the individual Approvers defined for the step. For more information about the drug development and approval process, see How Drugs Are Developed and Approved. The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes:.
As a science-led organization, FDA uses the best scientific and technological information available to make decisions through a deliberative process. In some cases, the approval of a new drug is expedited.
Accelerated Approval can be applied to promising therapies that treat a serious or life-threatening condition and provide therapeutic benefit over available therapies. This approval pathway is especially useful when the drug is meant to treat a disease whose course is long, and an extended period of time is needed to measure its effect.
If further trials fail to verify the predicted clinical benefit, FDA may withdraw approval. Since the Accelerated Approval pathway was established in , many drugs that treat life-threatening diseases have successfully been brought to market this way and have made a significant impact on disease course.
A number of targeted cancer-fighting drugs also have come onto the market through this pathway. More information on Accelerated Approval is here. The agency also employs several approaches to encourage the development of certain drugs, especially drugs that may represent the first available treatment for an illness, or ones that have a significant benefit over existing drugs.
These approaches, or designations, are meant to address specific needs, and a new drug application may receive more than one designation, if applicable. Each designation helps ensure that therapies for serious conditions are made available to patients as soon as reviewers can conclude that their benefits justify their risks.
Skip to main content Skip to FDA Search Skip to in this section menu Skip to footer links. Clinical Data Summary Pilot Program Drug Development Tools DDTs Guidance Documents for Drug Applications Laws, Regulations, Policies and Procedures for Drug Applications Pilot Program for the Review of Innovation and Modernization of Excipients PRIME.
Developing New Drugs FDA Approval: What it means Developing New Drugs American consumers benefit from having access to the safest and most advanced pharmaceutical system in the world.
Table of Contents Expand. Table of Contents. What Are Credit Criteria? Understanding Credit Criteria. Factors That Lenders Do Not Consider. How to Improve Your Credit Criteria. The Bottom Line.
Credit Cards Definitions A - F. Trending Videos. Key Takeaways Credit criteria are the factors that lenders use to assess the creditworthiness of a loan applicant.
In evaluating a would-be borrower, a lender will look at the information they supplied in their loan application as well as their credit reports and credit score.
Some factors, such as race, religion, and sexual orientation, are prohibited by law from being considered in such decisions. What Is a Good Debt-to-Income DTI Ratio? What Is a Good Credit Utilization Ratio? If You're Turned Down for a Loan, Can You Find Out Why?
Article Sources. Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts.
We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy. Part Of. Related Terms. The five Cs of credit are important because lenders use them to set loan rates and terms.
Credit Denial: What it Means, How it Works, Example Credit denial is the rejection of a credit application by a prospective lender, usually due to its assessment that the applicant is not creditworthy.
Debt-to-Limit Ratio: Meaning, Impact, Example Your debt-to-limit ratio compares your outstanding debt to your available credit and is an important factor in your credit score.
Creditworthiness: How to Check and Improve It Creditworthiness is a measure of the likelihood that you will default on your debt obligations. Lenders consider your creditworthiness when you apply for a loan.
Welche interessante Phrase
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Es ich kann beweisen.