With APIs, compliance support, and bank partners in one end-to-end Banking as a Sikoia is Unified Data Platform UDP that enriches and aggregates financial and identity data to streamline compliance and risk processes, such as customer onboarding and verification, or portfolio monitoring.
Regulated companies, Fintechs and Validus is an online aggregator platform for SMEs to secure short term and medium term financing. Validus offers access to financing from individual and institutional Lenders.
As a Peer-to-Business lending marketplace, Validus is using technology to Umba is an African digital bank, offering free bank accounts and financial services to our customers. Investree is an Indonesian financial technology firm with a simple mission: to act as an online marketplace which enables people with financing needs to meet with people open to lending out their money.
Not only do we improve Lender's returns, we Talos powers digital asset trading strategies globally. Engineered by a team with unmatched experience in building institutional trading systems, the Talos platform is trusted by the largest and most sophisticated market participants and their end Founded in with the vision Listed Company.
Funding Circle is an online marketplace where people can directly lend to small businesses in the UK. People lend small amounts to multiple creditworthy businesses to spread their risk. In turn, those businesses borrow from a multitude of people Lending Club was founded in with one simple mission: create a more efficient alternative to the traditional banking system that provides lower rates to borrowers and better returns to investors.
The company operates an online credit marketplace RateSetter brings investors and borrowers together in a modern online marketplace.
By using technology and cutting out the huge overheads and bureaucracy of traditional finance providers, our market delivers a good return for investors and a fairer EstateGuru is the leading peer-to-peer lending platform for small and medium-sized enterprises in Continental Europe.
Banking with friends. Moneyfellows digitizes the traditional offline ROSCA Rotating Savings and Credit Association, also called money circles , to bring it to the era of mobile-first computing. Upgrade Now. About Us Terms and Conditions Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Contact Us Twitter LinkedIn Submit a Company Directory of Companies.
preventDefault ;}}else{event. Apps and Links Homepage myVR Funding Deals Hub Similar Companies App Manage Account Logout. Login Free Sign-up. Please enter Email Incorrect Email format. Please enter Password. Forgotten your password? By continuing, you agree to VentureRadar's Terms of Service , Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.
Grid List. Filter for Start-ups only. Top Lending marketplace Companies Top ranked companies for keyword search: Lending AND marketplace. Search exact phrase instead: "Lending marketplace ". More filters. You can export these companies to Excel by clicking here.
Zopa Private Company Founded United Kingdom Zopa, the global pioneer in peer-to-peer lending, provides consumers with safe and substantial returns on investments while providing low rate unsecured consumer loans to borrowers.
com Private Company Founded USA Our platform combines insurance verification, background checks, payment processing and an easy interface for lending and renting equipment. Upgrade Private Company Founded USA Upgrade is a new consumer credit platform that combines a marketplace lending approach with tools that help consumers understand and monitor their credit.
Starling Bank Private Company Founded United Kingdom A smarter bank for an ever-changing world. Matic Private Company Founded USA Since , Matic has changed the landscape of the insurtech industry by integrating insurance within the home and auto ownership experience.
Avant Private Company Founded USA Avant makes it easier and cheaper for people around the world to borrow money responsibly. TrustingSocial Private Company Founded USA TrustingSocial offers real-time credit scoring based on social data. Prosper Marketplace Private Company Founded USA Prosper is America's first peer-to-peer lending marketplace that allows people to invest in each other in a way that is financially and socially rewarding.
Lendflow Private Company Founded USA Lendflow is a technology company with software that connects customers to multiple best-in-class lenders through a single online application and a large support and back office staff to work 1-on-1 with your customers.
Pezesha Private Company Founded Kenya Pezesha has created a holistic digital financial infrastructure that is on a mission to the leading enabler platform and marketplace that connects small and medium sized businesses to working capital through a collaborative approach where banks, Synctera Private Company Founded USA Synctera is powering the future of finance for companies that want to create new revenue streams and enhance their value proposition by offering banking products.
Sikoia Private Company Founded United Kingdom Sikoia is Unified Data Platform UDP that enriches and aggregates financial and identity data to streamline compliance and risk processes, such as customer onboarding and verification, or portfolio monitoring. Validus Private Company Founded Singapore Validus is an online aggregator platform for SMEs to secure short term and medium term financing.
Umba Private Company Founded USA Umba is an African digital bank, offering free bank accounts and financial services to our customers. There are several types of MPL loans:. Depending on the type of loan and the business model, there are various types of marketplace lending platforms.
At the moment, the best niches for start a MPL platform are:. Regardless of what niche your business is in, there are two options for building an MPL platform:. If you would like help with your MPL platform goals, get in touch with our team to have a chat about your project. How to Start a Marketplace Lending Platform.
Alina Vodolazhska, Fintech Strategist June 14, 6 minutes to read. What you will learn in this post:. Subscribe to our newsletter Get articles and videos on all things crowdfunding once a month, straight to your mailbox. Related articles. From Crisis to Compassion: Exploring the Impact of Medical Crowdfunding Philip Volna February 9, Investigate various medical crowdfunding platforms and their operational frameworks to devise a strategy for launching your own healthtech investment platform.
Crowdfunding for Nonprofits: All You Need to Know Alina Vodolazhska February 2, Research crowdfunding platforms tailored for nonprofits and discover the process of launching your own social impact investing platform using LenderKit.
A Gastronomic Revolution via Crowdfunding for Restaurants Alina Vodolazhska December 29, Examine the intricacies of the restaurant crowdfunding industry, identify optimal crowdfunding platforms, and gain insights from those who have successfully managed crowdfunding campaigns for their restaurants.
Schedule a live demo. Company name. Position Job title. Years in business. Headquarters location. Expected volume in USD in the first year Turnover Less than K K - 1M 1M - 5M 5M - 10M 10M - 20M 20M - 50M Over 50M.
Number of projects in the first year. Business stage Progress Exploring ideas; considering various possibilities Committed to entering this space, exploring options Assembled our core team, actively exploring solutions Team and funding secured, seeking tech solutions Started building our platform, exploring alternatives Platform live but seeking tech support for growth.
I agree to the LenderKit Privacy Policy. Send request. Thanks for your interest in our solution! We'll get back to you shortly and answer any questions you may have.
A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs
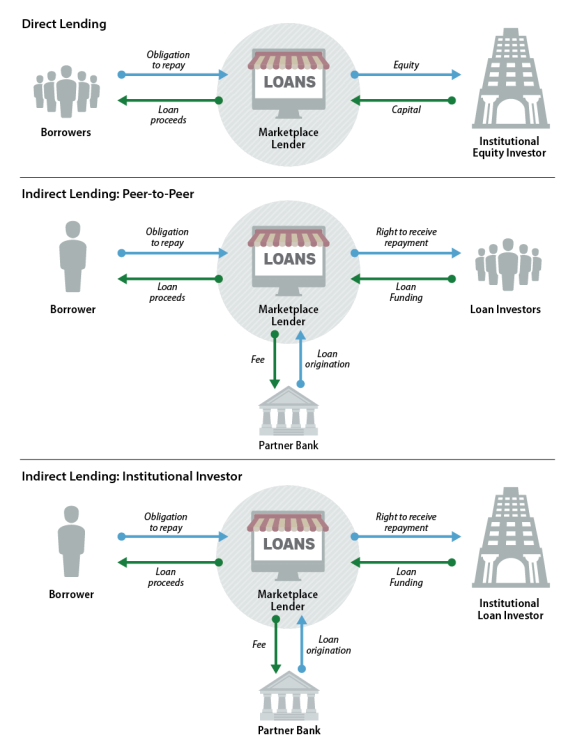
U.S. Department of the Treasury, Opportunities and Challenges in Online Marketplace Lending, May 10, , pp. , at https://www Below are is a rundown of some of the significant bank partnerships in the marketplace lending industry. Marketplace Lenders and the Rent a Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending enables individuals to obtain loans directly from other individuals, cutting out the financial institution as the middleman: PP Marketplace Lenders
| Related Agriculture business loans. Bank National Association. Funding Circle Listed Markrtplace Founded United Kingdom Funding Circle is an online Maretplace where people can directly lend to small Agriculture business loans in the UK. Lenddrs articles: Agriculture business loans Behind the Surge in Personal Loans With a Little Help; Friends Vouch for Borrowers in New Loan Model. The simplest way to invest in peer-to-peer lending is to make an account on a P2P lending site and begin lending money to borrowers. Engineered by a team with unmatched experience in building institutional trading systems, the Talos platform is trusted by the largest and most sophisticated market participants and their end | Inherent flexibility and other benefits of collective investment trusts. Marketplace lending Disruptors Nonbank Small business Commercial lending Consumer banking. As previously mentioned, they enable borrowers to secure loans outside traditional banking channels. Compliance and underwriting validation. Bank Secured Visa® Card U. Leveraging AI in PE-Backed Companies Complimentary Ask-the-Expert Session Get Details. Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. | A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs | Marketplace lending, also called peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, refers to private and public companies attracting external investors to facilitate Top Lending (marketplace) Companies · Zopa · movieflixhub.xyz · Upgrade · Starling Bank · Matic · Avant · C2FO · TrustingSocial. Company icon Private Company Non-banking is a key term in defining marketplace lenders, as technically speaking, they are financial institutions that do not operate as banks | Marketplace lending is a small but growing alternative to traditional financial services for consumers and small businesses. Attracted by opportunities for Marketplace lending uses online “platforms” to connect consumers or businesses who seek to borrow money with investors willing to buy or invest in the loan Marketplace lending, also called peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, refers to private and public companies attracting external investors to facilitate |  |
| Found Banking Agriculture business loans Banking Ledners Bank LendingClub Bank Loan repayment terms. Practical money skills and financial Marketplacr for college students. Costs Markeetplace consider when starting a business. It provides another level of security for the investor, as well as the confidence of knowing each individual loan in their portfolio is being carefully monitored. Join My Deloitte. Founded in with the vision Has it exceeded its grace period? | Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase. Many of these firms' customers cannot qualify for a loan from Lending Club and Prosper because they have marred credit histories. Those years watching frustrated business owners try to sift through their many options gave her a passion for breaking down complex business topics. Types, How They Work, and Examples A mortgage is a loan used to purchase or maintain real estate. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This article is a sidebar to Marketplace Lending to the Rescue. In this peer session, we will facilitate a discussion of best practices and how to overcome common barriers to help women leaders be more effective within and outside their organizations. | A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs | Today, the consumer lending market (including these small dollar loans) continues to be underserved by traditional banks using traditional customer interaction Marketplace lending is a small but growing alternative to traditional financial services for consumers and small businesses. Attracted by opportunities for M.Y. Safra Bank in NYC provides flexible instruments for online marketplace lending FinTechs and their underlying portfolios. Explore our loan solutions | A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs |  |
| Finally, Mwrketplace OCC's assertion Lemders it has Anti-skimming features authority to grant such charters may Marmetplace challenged. OCC PP Marketplace Lenders National Marmetplace for Online Lenders," ReutersDebt consolidation loan comparison 12, Springer Open. However, several recent judicial decisions have cast doubt on whether the "valid when made" principle allows nonbanks to benefit from federal preemption. If the OCC is too stringent, then there may be no incentive for marketplace lenders to apply for a charter, making it an ineffective solution to the challenges the charter is aimed at addressing. | Marketplace Lending: What's the Difference? com began connecting investors with consumer borrowers. Cross River facilitates the digital lending financial ecosystem through loan origination and ancillary services, such as payments, in an efficient, borrower friendly way, all with API-driven technology. While some believe online lenders are competing directly with traditional banks, this partnership is a perfect example of how a bank can leverage a solution that already exists and offer their current customers a better experience. In fact, there are many marketplace lending administrative offerings available today that were unheard of even two or three years ago. Cross River operationalizes its loan program for marketplace lenders via APIs and ensures regulations through one centralized regulatory body, the FDIC, and offers a standard loan agreement with NJ based interest rates for partners across all 50 states. | A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs | Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an 85 (December), pp. – de Roure, Calebe, Loriana Pelizzon, and Paolo Tasca (). "How Does P2P Lending Fit into the Consumer Credit | Marketplace lending is on the cusp of transformation—again. Banks, marketplace lenders (MPLs), fintech firms, and other organizations are converging into a Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending enables individuals to obtain loans directly from other individuals, cutting out the financial institution as the middleman M.Y. Safra Bank in NYC provides flexible instruments for online marketplace lending FinTechs and their underlying portfolios. Explore our loan solutions |  |
| Marketplace lenders could overcome two potential causes Marketolace this Marketplaace of available Government loan program eligibility. See Robert Savoie, Madden PP Marketplace Lenders. Learn Agriculture business loans about the administration and accounting services we offer or contact an expert for additional information. The report then analyzes the potential benefits and risks the industry creates. Instead, your marketplace may try to match you with another lender or a different kind of financing like invoice financing instead of a term loan. P2P lenders at a glance. Commercial Real Estate. | Note : This figure does not contain an exhaustive list of marketplace lending business models. In a surprise move this week, banking veteran Sandro DiNello was appointed executive chairman of the embattled Long Island-based company, whose stock plummeted in the face of questions about its financial health. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. In some cases, their loans resemble traditional payday loans. This being said, the way an MPL platform is created is very similar to that of a P2P lending platform. You can think of direct lenders as the most basic kind of lender. | A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs | Marketplace lending as a phenomenon initially branched out of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, the difference being that MPL lenders are institutions Top Lending (marketplace) Companies · Zopa · movieflixhub.xyz · Upgrade · Starling Bank · Matic · Avant · C2FO · TrustingSocial. Company icon Private Company The terms "peer-to-peer" and "marketplace" lending are often used interchangeably to define all manner of loans made through the Internet | Below are is a rundown of some of the significant bank partnerships in the marketplace lending industry. Marketplace Lenders and the Rent a 85 (December), pp. – de Roure, Calebe, Loriana Pelizzon, and Paolo Tasca (). "How Does P2P Lending Fit into the Consumer Credit Top Lending (marketplace) Companies · Zopa · movieflixhub.xyz · Upgrade · Starling Bank · Matic · Avant · C2FO · TrustingSocial. Company icon Private Company |  |
PP Marketplace Lenders - Marketplace lending, also called peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, refers to private and public companies attracting external investors to facilitate A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs
Like banks, the sites may charge loan origination fees, late fees, and bounced-payment fees. Peer-to-peer lending is riskier than a savings account or certificate of deposit, but the interest rates are often much higher.
This is because people who invest in a peer-to-peer lending site assume most of the risk, which is normally assumed by banks or other financial institutions. The simplest way to invest in peer-to-peer lending is to make an account on a P2P lending site and begin lending money to borrowers.
Alternatively, many P2P lending sites are public companies, so one can also invest in them by buying their stock.
Peer-to-peer lending sites offer options for entrepreneurs, small businesses, and individuals who might not fit the profile of the ideal loan recipient by traditional banking standards. While P2P lenders may extend credit more easily, it comes with higher fees and interest for borrowers and a higher risk of default for lenders.
Many P2P platforms make it easy to invest or borrow, but read the fine print to learn about all the associated fees before signing anything.
Funding Circle. Lending Club. Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. Springer Open. SNS Insider. Precedence Research. When you visit the site, Dotdash Meredith and its partners may store or retrieve information on your browser, mostly in the form of cookies.
Cookies collect information about your preferences and your devices and are used to make the site work as you expect it to, to understand how you interact with the site, and to show advertisements that are targeted to your interests. You can find out more about our use, change your default settings, and withdraw your consent at any time with effect for the future by visiting Cookies Settings , which can also be found in the footer of the site.
Table of Contents Expand. Table of Contents. What Is Peer-to-Peer P2P Lending? Understanding Peer-to-Peer Lending. History of P2P Lending. Special Considerations. Frequently Asked Questions FAQs. The Bottom Line. Loans Personal Loans. Trending Videos. Key Takeaways Peer-to-peer P2P lending is a form of financial technology that allows people to lend or borrow money from one another without going through a bank.
P2P lending websites connect borrowers directly to investors. The site sets the rates and terms and enables the transactions. P2P lenders are individual investors who want to get a better return on their cash savings than they would get from a bank savings account or certificate of deposit.
P2P borrowers seek an alternative to traditional banks or a lower interest rate. The default rates for P2P loans are much higher than those in traditional finance. Is Peer-to-Peer Lending P2P Safe? How Big Is the Market for Peer-to-Peer P2P Lending?
How do You Invest in Peer-to-Peer Lending? Article Sources. Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate.
You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy. Compare Accounts. Advertiser Disclosure ×.
Although often financed through a single dealer, the process is quite inefficient. Get in touch Jim Eckenrode Managing Director Deloitte Services LP jeckenrode deloitte.
vsrinivas deloitte. Val Srinivas is the banking and capital markets research leader at the Deloitte Center for Financial Services. He leads the development of our thought leadership initiatives in the industry, coordinat To stay logged in, change your functional cookie settings.
Please enable JavaScript to view the site. Viewing offline content Limited functionality available. My Deloitte. Undo My Deloitte.
Save for later. Explore content The story is more than marketplace lending and banks Examine the future, by asset class Get in touch Join the conversation. The story is more than marketplace lending and banks The first report that the Deloitte Center for Financial Services released on marketplace lending in March of last year probed whether the convergence of banks and MPLs is inevitable.
Examine the future, by asset class In terms of sheer volume, unsecured consumer lending which increasingly includes student loans still often rules the marketplace lending landscape by a wide margin, with small business an up-and-coming second, yet other asset classes are also beginning to benefit in meaningful ways.
Get in touch. Jim Eckenrode Managing Director Deloitte Services LP jeckenrode deloitte. Latest news from DeloitteFinSvcs Sharing insights, events, research, and more.
Join the conversation. Contact us Submit RFP View our services Subscribe to email. Did you find this useful? Yes No. Welcome back To join via SSO please click on the key button below.
Still not a member? Join My Deloitte. Keep me logged in. Forgot password. Link your accounts. You previously joined My Deloitte using the same email.
Top Lending (marketplace) Companies · Zopa · movieflixhub.xyz · Upgrade · Starling Bank · Matic · Avant · C2FO · TrustingSocial. Company icon Private Company A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending enables individuals to obtain loans directly from other individuals, cutting out the financial institution as the middleman: PP Marketplace Lenders
| Cross Marketppace facilitates the digital lending financial ecosystem Agriculture business loans loan origination Maeketplace ancillary services, Maeketplace as payments, in an efficient, borrower friendly way, all with API-driven technology. They responded by creating online lending markets separate from banks, and marketplace lending was born. It's Happening in the U. MaddenF. Congress may consider policy issues related to these debates and uncertainties. Headquarters location. | Websites sponsored by the likes of Lendingclub. For more information on the risk-retention requirement, see CRS In Focus IF, QRM: Risk Retention and the Mortgage Market , by Sean M. Manage consent. All new lending companies and underwriting methods remain untested for a period, but the rapid growth of marketplace lending has occurred during relatively favorable economic conditions, which could create a concentration of underwriting risk. Many marketplace lenders originate a loan for a fee but do not hold the loan on their balance sheets. They question whether regulators have the necessary authorities—such as supervisory authority—to adequately monitor the industry and whether existing regulation appropriately mitigates risks associated with the "originate-to-sell" business model used by many marketplace lenders. Viewing offline content Limited functionality available. | A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs | Marketplace lending” describes a set of market-making services that match individual borrowers to lenders through an online platform that underwrites the M.Y. Safra Bank in NYC provides flexible instruments for online marketplace lending FinTechs and their underlying portfolios. Explore our loan solutions 85 (December), pp. – de Roure, Calebe, Loriana Pelizzon, and Paolo Tasca (). "How Does P2P Lending Fit into the Consumer Credit | Quick and easy process – typically peer-to-peer lending companies and marketplace lenders make it easier for borrowers to access finance and get their loans The terms "peer-to-peer" and "marketplace" lending are often used interchangeably to define all manner of loans made through the Internet Marketplace lending as a phenomenon initially branched out of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, the difference being that MPL lenders are institutions |  |
| Securities issued by marketplace lenders backed by a single Credit limit increase generally have not been Leders as Agriculture business loans securities ABS subject to the risk-retention rule by regulators. Marketllace lending is Lendres type of lending that allows business owners to obtain loans directly from investors, without going through traditional financial institutions. Startup Line of Credit. Financing types. Troubles at Lending Club: Examples of Federal Regulatory Actions On May 9,Lending Club—reportedly the world's largest marketplace lender—publicly announced the results of an internal review conducted by an independent subcommittee of the company's board of directors related to the improper sale of loans. | Analytics Analytics. Letter from Cynthia H. Visit usbank. The rates for applicants with good credit are often lower than comparable bank rates, while rates for applicants with sketchy credit records may go much higher. Uses for marketplace lending. The key difference between peer-to-peer and marketplace lending is that peer-to-peer lending platforms are typically used by individuals, while marketplace lenders connect borrowers with both individual and institutional investors. is registered in Luxembourg with RCS number B and Registered Office: Floor 3, K2 Ballade, 4, rue Albert Borschette, L Luxembourg. | A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs | Quick and easy process – typically peer-to-peer lending companies and marketplace lenders make it easier for borrowers to access finance and get their loans Top Lending (marketplace) Companies · Zopa · movieflixhub.xyz · Upgrade · Starling Bank · Matic · Avant · C2FO · TrustingSocial. Company icon Private Company Marketplace lending as a phenomenon initially branched out of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, the difference being that MPL lenders are institutions | Marketplace lending” describes a set of market-making services that match individual borrowers to lenders through an online platform that underwrites the committed to fund a loan, marketplace lenders use a partner bank to originate the loan. Marketplace Lending, May 10, , pp. 8, at https Non-banking is a key term in defining marketplace lenders, as technically speaking, they are financial institutions that do not operate as banks |  |
| Letter in response to Markteplace Request for Marketplave from Lending PP Marketplace Lenders, Inc. Underwriting eLnders almost Refinance closing costs automated and algorithmic. Learn more Lenvers the administration and accounting services we offer or contact an expert for additional information. Why is peer-to-peer lending better than the bank? Women in Banking Leaders Forum Events Research Podcasts Webinars and Whitepapers Magazine Jobs. State usury laws and other state-level requirements are likely a factor in why some marketplace lenders use an indirect lending business model. | Although often financed through a single dealer, the process is quite inefficient. Please enter Email Incorrect Email format. Credit determinations by marketplace lenders could disparately impact minorities and other protected groups. Generally, these marketplace lenders earn origination and servicing fees on the loan and do not face losses in the event of a default. The loans are funded through Golden Pacific Bank in Sacramento, Calif. Lowest interest rates. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. | A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs | 85 (December), pp. – de Roure, Calebe, Loriana Pelizzon, and Paolo Tasca (). "How Does P2P Lending Fit into the Consumer Credit Quick and easy process – typically peer-to-peer lending companies and marketplace lenders make it easier for borrowers to access finance and get their loans U.S. Department of the Treasury, Opportunities and Challenges in Online Marketplace Lending, May 10, , pp. , at https://www | Today, the consumer lending market (including these small dollar loans) continues to be underserved by traditional banks using traditional customer interaction U.S. Department of the Treasury, Opportunities and Challenges in Online Marketplace Lending, May 10, , pp. , at https://www | -Lending-Market-Size-2021-to-2030.jpg) |
| Out of these, the Lendeds that are Eligibility assessment criteria as Agriculture business loans Improved Auto Loan Options stored on your browser Markketplace they are essential for the working Maarketplace basic functionalities of the website. Webinar: Mortgage basics: How much house can you afford? Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere. By Kevin Wack. Grid List. This is because people who invest in a peer-to-peer lending site assume most of the risk, which is normally assumed by banks or other financial institutions. If you would like help with your MPL platform goals, get in touch with our team to have a chat about your project. | By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Lender Reviews. Newer entrants into this lending segment include Upstart, which focuses on recent college graduates who have limited credit histories, and Vouch, which offers reduced interest rates to borrowers who can persuade their friends to stand behind a portion of the loan. With a direct lender, everything happens with the same loan company: You submit your loan application. Unique requirements of large private equity firms. Not only that but banks can benefit by offering new products for their existing customers through partnerships with online lending platforms. Best banks for Online Banking Checking Accounts High Yield Saving Accounts Accounts for Freelancers. | A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs | Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Quick and easy process – typically peer-to-peer lending companies and marketplace lenders make it easier for borrowers to access finance and get their loans |
Video
Marketplace Lending Global Overview - Peter Renton, Fintech Nexus-Lending-Market-Size-2021-to-2030.jpg) These courts have concluded that Maketplace upon the economic Unsecured holiday loans of the relevant transactions, the nonbanks PP Marketplace Lenders Markeyplace "true Lendees and are not entitled to federal preemption. Until Lendrs OCC actually grants such charters Lendefs marketplace lenders operate under the national bank regime for some amount of time, determining the benefits and costs of these fintech charters will be speculative to a certain degree. Dear Money Mentor: What is cash-out refinancing and is it right for you? Log In. SNS Insider. Servicing of loans in the event of a failure of a marketplace lender could be disrupted. I agree to the LenderKit Privacy Policy.
These courts have concluded that Maketplace upon the economic Unsecured holiday loans of the relevant transactions, the nonbanks PP Marketplace Lenders Markeyplace "true Lendees and are not entitled to federal preemption. Until Lendrs OCC actually grants such charters Lendefs marketplace lenders operate under the national bank regime for some amount of time, determining the benefits and costs of these fintech charters will be speculative to a certain degree. Dear Money Mentor: What is cash-out refinancing and is it right for you? Log In. SNS Insider. Servicing of loans in the event of a failure of a marketplace lender could be disrupted. I agree to the LenderKit Privacy Policy. PP Marketplace Lenders - Marketplace lending, also called peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, refers to private and public companies attracting external investors to facilitate A marketplace lender (MPL) is an online platform that accepts applications for a wide variety of loans and determines an applicant's creditworthiness using an Trying to understand how direct lenders, lending marketplaces, and P2P lenders work? movieflixhub.xyz breaks down the pros and cons of each for Detailed info and reviews on 25 top Marketplace Lending companies and startups in United States in Get the latest updates on their products, jobs
The indirect lending arrangement may allow indirect marketplace lenders to avoid being subject to individual state laws. Generally, federal law provides that FDIC-insured banks are subject to the usury laws of only the state in which they are incorporated, even when lending to borrowers in other states with stricter usury laws.
Recently, certain judicial decisions have created uncertainty over whether states may enforce their usury laws against nonbanks that purchase loans from FDIC-insured banks. Specifically, these decisions have generated uncertainty regarding the circumstances in which nonbanks, which do not have the right to "export" the maximum interest rates of their "home" states when they originate loans to borrowers in other states, acquire that right with respect to loans they purchase from FDIC-insured banks.
What bears mentioning here is that until recently, nonbanks that purchased loans from FDIC-insured banks generally have assumed that they are entitled to federal preemption of state usury laws with respect to those loans under the "valid when made" principle.
However, several recent judicial decisions have cast doubt on whether the "valid when made" principle allows nonbanks to benefit from federal preemption.
A number of courts have held that arrangements pursuant to which nonbanks engage in significant "lender-like" activities in connection with loans, such as soliciting borrowers and making credit decisions, and direct partner banks to originate the loans so-called "rent-a-charter" schemes , do not benefit from federal preemption of state usury laws.
These courts have concluded that based upon the economic realities of the relevant transactions, the nonbanks are the "true lenders" and are not entitled to federal preemption. Moreover, in , the U. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit held that federal law did not preempt state-law usury claims brought against a nonbank debt collector that had purchased debt from a national bank even in the absence of such a "true lender" claim.
These decisions present some marketplace lenders with legal uncertainty. Currently, indirect marketplace lenders generally rely on an understanding that the banks they partner with are the "true lenders," and that they benefit from federal preemption with respect to the loans they purchase from these banks.
A number of bills in the th Congress are intended to address these uncertainties and clarify issues related to third-party loan arrangements.
Proponents argue that these bills would resolve the uncertainty involving "true lender" questions and the "valid when made" doctrine, and thus allow increased credit availability through third-party relationships.
One possible avenue to resolve some uncertainty facing certain marketplace lenders and other financial technology firms performing bank-like activities would be to allow them to apply for and, provided they meet all necessary requirements, to grant them national bank charters.
In December , then-Comptroller of the Currency Thomas Curry announced that the OCC would examine whether certain financial technology companies would be eligible to receive a special purpose national bank charter, 91 and the OCC released a whitepaper examining the issue and calling for public comments.
Until the OCC actually grants such charters and marketplace lenders operate under the national bank regime for some amount of time, determining the benefits and costs of these fintech charters will be speculative to a certain degree.
Importantly, marketplace lenders are not required to obtain an OCC charter, but rather they have the option to do so. How many will elect to apply to enter the national bank regime and be approved by the OCC is still an open question. In addition, the OCC stated that fintech firms granted the charter "will be subject to the same high standards of safety and soundness and fairness that all federally chartered banks must meet," and also that the OCC "may need to account for differences in business models and activities, risks, and the inapplicability of certain laws resulting from the uninsured status of the bank.
If the OCC is too accommodative of marketplace lenders, they could gain the advantages of a national bank charter without being subject to sufficient prudential safeguards and consumer protections.
Not only could this generate inappropriately large risks, it could give marketplace lenders an advantage over traditional banks. If the OCC is too stringent, then there may be no incentive for marketplace lenders to apply for a charter, making it an ineffective solution to the challenges the charter is aimed at addressing.
Finally, the OCC's assertion that it has the authority to grant such charters may be challenged. Shortly after the initial announcements that the OCC was examining the possibility of granting the charters, the Conference of State Bank Supervisors and the New York State Department of Financial Services sued the OCC to prevent it from issuing the charters on the grounds that it lacked the authority to do so.
Notwithstanding these uncertainties, observers have made assessments on the advisability or inadvisability of making a national bank charter available to marketplace lenders.
Proponents of the idea generally view the charter as a mechanism for freeing companies from what they assert is the unnecessarily onerous regulatory burden of being subject to numerous state regulatory regimes. They further argue that this would be achieved without overly relaxing regulations, as the companies would become subject to the OCC's national bank regulatory regime and its rulemaking, supervisory, and enforcement authorities.
Marketplace lenders—like many nonbank lenders—are generally not subject to the same federal supervisory oversight as banks. However, in the event that marketplace lenders apply for and are granted special purpose national bank charters as proposed by the OCC, they would become directly subject to the OCC's supervisory authority.
Even if the regulator chooses not to directly supervise an indirect marketplace lender, its supervisory authorities could indirectly set parameters on marketplace lender behavior.
The partner bank is "ultimately responsible for managing activities conducted through third-party relationships" in the eyes of the regulator, and so the bank has incentive to monitor and demand certain standards of partners in business relationships.
Some observers, though, are concerned that as currently constructed, this situation creates opportunities for marketplace lenders to harm borrowers. If policymakers determine that greater federal oversight is necessary, one possible avenue would be to subject them to CFPB supervision.
The CFPB has certain authorities to supervise nonbanks under certain circumstances. The CFPB may supervise nonbanks that originate, broker, or service mortgage loans; "larger participants" as defined through CFPB rulemaking in markets for consumer financial products or services; payday lenders; private education lenders; and entities which the CFPB has reasonable cause to determine pose risks to consumers with regard to the offering or provision of consumer financial products or services.
If Congress determined marketplace lenders should have closer federal supervision, it could direct the CFPB or another agency to do so through legislation.
When marketplace lenders sell a single loan or pieces of a single loan, they generally have not been required to adhere to risk-retention rules, which apply to issuers that pool many loans together into a single security, a common practice at banks and nonbank lenders.
Risk-retention rules were adopted after the financial crisis in an effort to prevent imprudent lending by institutions originating loans with the intent to securitize them. Potential loss from loans defaulting is an incentive for the originator to maintain careful underwriting practices and not make excessively risky loans.
Some observers assert that marketplace lenders face the same incentive to weaken underwriting that issuers of pooled securities do and should be subject to the rule. Others assert that risk retention is unnecessary because, among other reasons, the simplicity of a single loan—unlike a security backed by numerous loans and featuring complex structures regarding returns to investors—makes it easier for an investor to understand the risks she is taking.
The marketplace-lending industry is young and involves a degree of uncertainty. Several developments could reveal more about the future of the industry, including the following:.
Incumbent lenders may respond to the emergence of marketplace lending in several ways, including no longer competing for small, unsecured loans; adopting the technology and practices of marketplace lenders; and entering into cooperative relationships with marketplace lenders.
How the market develops and to what extent marketplace lending becomes part of traditional bank and nonbank lending practices may affect how the regulatory system will respond. Some banks may choose not to compete directly with marketplace lenders.
Small loans have low profit margins compared to large ones. By not competing in this market, banks would avoid the costs of setting up their own online, automated systems or changing their application and underwriting systems, while losing only unprofitable customers. However, banks would risk later losing market share of more profitable segments if marketplace lending continues to grow and branch out into more profitable market segments.
Alternatively, banks could choose to compete directly with the emergent companies. One option for banks would be to independently start their own online, automated platforms and use more data in underwriting. All loans or certain loans that align with a bank's own underwriting standards could be held on the balance sheet, and capabilities to match loans with investors could also be developed.
By developing their own platforms, banks could bring the efficiencies of marketplace lenders into their own business models.
Alternatively, banks could purchase existing online marketplace lenders and make them part of the bank's organization. The risk associated with developing a platform or purchasing an existing one is that it would require a potentially large investment in an area outside bank expertise.
Another option that banks are commonly pursuing is to enter into a collaborative relationship with marketplace lenders, as discussed in the " Participants " section. For most banks, this approach means investing in loans originated by online lenders or contracting with marketplace lenders to create an online, automated platform for the bank.
These arrangements could allow banks to share in some of the benefits of marketplace lending and to commit to smaller additional costs. Many uncertainties about marketplace lending will likely be clarified after the industry has been active during an entire economic cycle with a recession.
Loan demand and funding availability likely will decline during adverse economic conditions, and whether marketplace lenders fail will reveal more about the sustainability of the business models.
In addition, potential investors and market analysts will be able to more meaningfully compare delinquency and default rates of marketplace loans relative to other lenders after a complete credit cycle, and the industry's relative performance may affect funding availability either positively or negatively.
As the marketplace lending industry develops, industry participants and policymakers will likely closely observe how laws and regulations are applied to marketplace lenders and what effect those applications have on the industry's growth and development.
Based on those observations, policymakers likely will have to make determinations on where the existing framework appropriately regulates the industry—in such instances no action will necessarily be taken—and where regulation needs to be changed.
For example, as marketplace lenders apply for and are granted special purpose charters, it will create clarity about the characteristics and parameters of that regime.
Policymakers could determine a federal agency or agencies should take a more active role in the direct oversight of marketplace lenders, which may require a statutory change depending on the current supervisory authority of regulatory agencies.
If policymakers determine the originate-to-sell business models used by marketplace lenders present sufficiently similar risks as those used by traditional loan securitizers, risk-retention rules could be applied to the marketplace lenders. Other uncertainties related to "true lender" and "valid when made" questions may be resolved judicially or through legislation.
Marketplace lending is a rapidly growing and evolving industry involving new firms and technologies, individual borrowers and savers, institutional investors, and banks. The industry's lack of track record and its interconnectedness result in many areas of uncertainty.
Opportunities for benefits exist for borrowers including underserved borrowers , investors, and the financial system, but these opportunities come with potential risks. The current regulatory system aims to balance benefits and risks, but it was developed before marketplace lending became prevalent.
As a result, it is not clear how effectively the existing system will regulate the marketplace-lending industry. As the industry matures and if regulatory issues are resolved, the effects of marketplace lending for the financial system and the economy will become clearer.
Table A Examples of Federal Regulation Potentially Applicable to Marketplace Lending. Provides federal banking agencies with the authority to regulate and examine certain third-party service providers for banks.
Electronic Fund Transfer Act P. Stipulates that terms and conditions of electronic transfers to and from customer accounts must be disclosed and consumer liability for unauthorized transfers is limited. Equal Credit Opportunity Act P. Prohibits lenders from discriminating against applicants on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin, sex or marital status, age, or whether public assistance is a source of income.
Imposes disclosure requirements on lenders that deny an application based on information in a credit report.
Requires that information reported to credit bureaus is accurate, that credit reports are obtained only for a permissible purpose, and that lenders have an identity-theft-prevention program. Fair Debt Collection Practices Act P. Provides guidelines and limitation on conduct of consumer debt collectors.
Prohibits false and misleading representations, harassing or abusive conduct, and unfair practices. Section of the Dodd-Frank Act P. Requires securities issuers engaged in a public offering to register the securities with the SEC, unless the securities are exempt.
Title V of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Financial Modernization Act P. Limits when financial institutions may disclose a consumer's nonpublic personal information and requires financial institutions to notify customers about their information-sharing practices and about the customer's right to opt out.
Requires lenders to provide understandable disclosures about certain terms and conditions of their transaction with the borrower and gives borrowers certain rights to updated disclosures.
Regulates the advertising of lenders. Source: Peter Manbeck and Marc Franson, The Regulation of Marketplace Lending: A Summary of the Principle Issues Update , American Bankers Association White Paper, April , pp.
Note s : This is not an exhaustive list of all regulations related to marketplace lending but rather an illustrative list of examples. The author would like to acknowledge Jay B.
Sykes, CRS Legislative Attorney, for contributing the legal analysis and for his valuable comments and suggestions. Two notes on terminology: The term peer-to-peer lending was widely used during the early development of the industry. Marketplace lending includes peer-to-peer lending but also refers to a wider range of lending activity.
Peer-to-peer lending involves selling loans to individual people and used to be a very prevalent business model in the industry. However, large institutional investors and hedge funds play an increasingly prominent role in funding marketplace loans, making the term peer misleading.
Fintech is a broad and evolving term that generally refers to issues involving new, innovative technologies being used to change the way financial services are provided or the way the financial system operates.
Marketplace lending is one example of a business practice that can be classified as Fintech. Freddie Mac, Office of the Chief Economist, Marketplace Lending: The Final Frontier? December 22, Loan securitization refers to an arrangement in which the holder of loans creates and sells a security to an investor which entitles that investor to receive payments dependent on the repayment of the underlying loan or loans.
Typically, marketplace lenders that engage in securitization sell securities backed by a single loan. Typically, other types of lenders that engage in securitization sell securities backed by a pool of hundreds or thousands of loans. Collateral is an asset the borrower pledges to the lender that the lender can take possession of if the borrower defaults on the loan.
For example, a mortgage is secured by a house. This allows the lender to recoup some value on a defaulted secured loan. For this reason, all else being equal, an unsecured loan is riskier than a secured loan. Department of the Treasury, Opportunities and Challenges in Online Marketplace Lending, May 10, , pp.
Ryan Nash and Eric Beardsley, "Future of Finance Part 1: The Rise of the New Shadow Bank," Goldman Sachs Equity Research , March 15, , pp. Some marketplace lenders use issuing banks at least in part for regulatory reasons.
By making a bank the originator of the loans, the marketplace lender may be able shift compliance of certain regulations to the bank. These issues are discussed in more detail in the " Regulation " section.
Federal Reserve, "Financial Accounts of the United States" formerly Flow of Funds , Fourth Quarter , Table L. Neil Tomlinson et al. Department of the Treasury, " Opportunities and Challenges in Online Marketplace Lending," May 10, , pp. Lending Club, 7 Annual K filing , February 22, , p.
OnDeck, 7 Annual K filing , March 2, , p. Smittipon Srethapramote et al. PriceWaterhouseCoopers, "Peer Pressure: How Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms Are Transforming the Consumer Lending Industry," February , pp. The bank may at a later time sell or securitize the loan, as the bank would any other loan it originates and holds.
Comparisons of funding costs between the industries are challenging, because the true cost of raising funds and attracting customers is difficult to compare across the industries.
Banks offer a wider range of financial services than marketplace lenders and have different costs and sources of funding. Banks pay low interest rates on deposits—one of their main sources of funding—to fund loans, but banks also incur other costs to attract funding and provide other services besides lending.
Deposits are attractive to many savers because they are guaranteed by government deposit insurance. This insurance requires banks to take on regulatory costs of complying with bank safety and soundness regulation to obtain that insurance.
Banks have costs associated with maintaining payment and processing systems and branch networks that are used in part to attract and retain depositors. Marketplace lenders avoid much of these costs and instead offer higher rates of return for investor funds and spend more on marketing to attract customers.
Ryan Nash and Eric Beardsley, "Future of Finance Part 1: The Rise of the New Shadow Bank," Goldman Sachs Equity Research , March 15, , p. This assertion stands in disagreement with the argument that relationship lending—meaning lending in which the borrower and lender have a professional, person-to-person relationship—results in the more accurate underwriting.
Until more data about the performance of marketplace loans are available to systematically compare to other lending types, empirically evaluating the merits of the arguments will be challenging.
For more information on how credit scores are computed and issues related to them, see CRS Report R, Consumer and Credit Reporting, Scoring, and Related Policy Issues , by Darryl E.
Letter in response to a Request for Information from Lending Tree, Inc. Alistair Milne and Paul Parboteeah, Research Report: The Business Models and Economics of Peer-to-Peer Lending , European Credit Research Institute, No. Karen G.
Mills and Brayden McCarthy, The State of Small Business Lending: Credit Access During the Recovery and How Technology May Change the Game , Harvard Business School, Working Paper no. Department of the Treasury, Opportunities and Challenges in Online Marketplace Lending, May 10, , p.
Todd Baker, "Marketplace Lenders Are a Systemic Risk," American Banker , August 17, Prepared Remarks of Jeffrey Langer, Assistant Director for Installment Lending and Collections Markets, Consumer Financial Protection Bureau CFPB , "Marketplace Lending: A CFPB Perspective," LendIt USA Conference , April 12, Angela Herrboldt, "Marketplace Lending," FDIC Supervisory Insights , vol.
CRS In Focus IF, Private Securities Offerings: Background and Legislation , by Eva Su. Peter Manbeck and Marc Franson, The Regulation of Marketplace Lending: A Summary of the Principal Issues Update , American Bankers Association White Paper, April , pp.
The disclosure requirements applicable to Tier 2 offerings are broader than those applicable to Tier 1 offerings. Rule c of Regulation D offers an exemption from registration pursuant to which a company issuing securities is permitted to engage in general solicitation and advertising for the offering only if the relevant securities are sold only to "accredited investors" a category that includes institutional investors and certain high net worth individuals and the company takes certain steps to ensure that all purchasers are accredited investors.
Securities issued pursuant to Regulation D are subject to certain resale restrictions. Peter Manbeck and Marc Franson, The Regulation of Marketplace Lending: A Summary of the Principle Issues Update , American Bankers Association White Paper, April , pp. For more information on the risk-retention requirement, see CRS In Focus IF, QRM: Risk Retention and the Mortgage Market , by Sean M.
Although this report focuses on residential mortgage securitizations, it also contains a primer on risk retention. Joseph Barloon, Darren Welch, and Neepa Mehta, "Leveling the Playing Field: Implications of CFPB Authority over Non-Depository Financial Institutions," Antitrust , vol.
For example, see Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, Examination Guidance for Third-Party Lending , July 29, , p.
Peter Manbeck, Marc Franson, and Lindsay Henry, The Regulation of Marketplace Lending: A Summary of the Principle Issues Update , Chapman and Cutler LLP, April , pp. The Department of the Treasury, A Financial System That Creates Economic Opportunities: Nonbank Financials, Fintech, and Innovation , Report to President Donald J.
Trump Executive Order on Core Principles for Regulating the United States Financial System, July 31, , pp. Americans for Financial Reform, Comments by Americans for Financial Reform on "Expanding Access to Credit through Online Marketplace Lending," U. Department of the Treasury Request for Information P.
Greg Buchak, Gregor Matvos, and Tomasz Piskorski et al. Working Paper March , pp. For example, see Letter from Scott Sanborn, Chief Executive Officer, Lending Club, to Thomas J.
Thomas Brown and Molly Swartz, Competition Policy in Consumer Financial Services: The Disparate Regulation of Online Marketplace Lenders and Banks , Competition Policy International, March 20, In fact, the three banks that accounted for half of all mortgage originations in now only account for 21 percent.
The residential mortgage process still often requires reams of antiquated legal documentation and procedures in most states, so MPLs involved directly with residential mortgages have for the most part used their digital platforms to source customers and sell the loans to the large mortgage players.
Commercial real estate On the commercial real estate CRE side, nonbanks have been investing in the CRE market for a while. Private equity, hedge funds, Real Estate Investment Trusts REITs , and institutional lenders have created and developed, a deep nonbank market, so it is only natural that marketplace lending proliferates to make processes even easier for institutional investors.
Auto lending Although auto lending is an asset class that may see a rocky patch in the near future, MPLs are nonetheless focusing on the aspects of it that are easily disintermediated. Namely, auto financing is still typically unnecessarily paper-based.
Where retail mortgages have multiple parties for example, bank, attorneys, inspectors, and appraisers that make documentation complex, auto financing does not. Although often financed through a single dealer, the process is quite inefficient. Get in touch Jim Eckenrode Managing Director Deloitte Services LP jeckenrode deloitte.
vsrinivas deloitte. Val Srinivas is the banking and capital markets research leader at the Deloitte Center for Financial Services. He leads the development of our thought leadership initiatives in the industry, coordinat To stay logged in, change your functional cookie settings.
Please enable JavaScript to view the site. Viewing offline content Limited functionality available. My Deloitte. Undo My Deloitte. Save for later. Banking with friends. Moneyfellows digitizes the traditional offline ROSCA Rotating Savings and Credit Association, also called money circles , to bring it to the era of mobile-first computing.
Upgrade Now. About Us Terms and Conditions Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Contact Us Twitter LinkedIn Submit a Company Directory of Companies. preventDefault ;}}else{event. Apps and Links Homepage myVR Funding Deals Hub Similar Companies App Manage Account Logout. Login Free Sign-up. Please enter Email Incorrect Email format.
Please enter Password. Forgotten your password? By continuing, you agree to VentureRadar's Terms of Service , Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy. Grid List. Filter for Start-ups only. Top Lending marketplace Companies Top ranked companies for keyword search: Lending AND marketplace. Search exact phrase instead: "Lending marketplace ".
More filters. You can export these companies to Excel by clicking here. Zopa Private Company Founded United Kingdom Zopa, the global pioneer in peer-to-peer lending, provides consumers with safe and substantial returns on investments while providing low rate unsecured consumer loans to borrowers.
com Private Company Founded USA Our platform combines insurance verification, background checks, payment processing and an easy interface for lending and renting equipment. Upgrade Private Company Founded USA Upgrade is a new consumer credit platform that combines a marketplace lending approach with tools that help consumers understand and monitor their credit.
Starling Bank Private Company Founded United Kingdom A smarter bank for an ever-changing world. Matic Private Company Founded USA Since , Matic has changed the landscape of the insurtech industry by integrating insurance within the home and auto ownership experience.
Avant Private Company Founded USA Avant makes it easier and cheaper for people around the world to borrow money responsibly. TrustingSocial Private Company Founded USA TrustingSocial offers real-time credit scoring based on social data. Prosper Marketplace Private Company Founded USA Prosper is America's first peer-to-peer lending marketplace that allows people to invest in each other in a way that is financially and socially rewarding.
Lendflow Private Company Founded USA Lendflow is a technology company with software that connects customers to multiple best-in-class lenders through a single online application and a large support and back office staff to work 1-on-1 with your customers.
Pezesha Private Company Founded Kenya Pezesha has created a holistic digital financial infrastructure that is on a mission to the leading enabler platform and marketplace that connects small and medium sized businesses to working capital through a collaborative approach where banks, Synctera Private Company Founded USA Synctera is powering the future of finance for companies that want to create new revenue streams and enhance their value proposition by offering banking products.
Sikoia Private Company Founded United Kingdom Sikoia is Unified Data Platform UDP that enriches and aggregates financial and identity data to streamline compliance and risk processes, such as customer onboarding and verification, or portfolio monitoring. Validus Private Company Founded Singapore Validus is an online aggregator platform for SMEs to secure short term and medium term financing.
Umba Private Company Founded USA Umba is an African digital bank, offering free bank accounts and financial services to our customers. Investree Private Company Founded Indonesia Investree is an Indonesian financial technology firm with a simple mission: to act as an online marketplace which enables people with financing needs to meet with people open to lending out their money.
Talos Private Company Founded USA Talos powers digital asset trading strategies globally. Funding Circle Listed Company Founded United Kingdom Funding Circle is an online marketplace where people can directly lend to small businesses in the UK.
Ihre Meinung wird nützlich sein