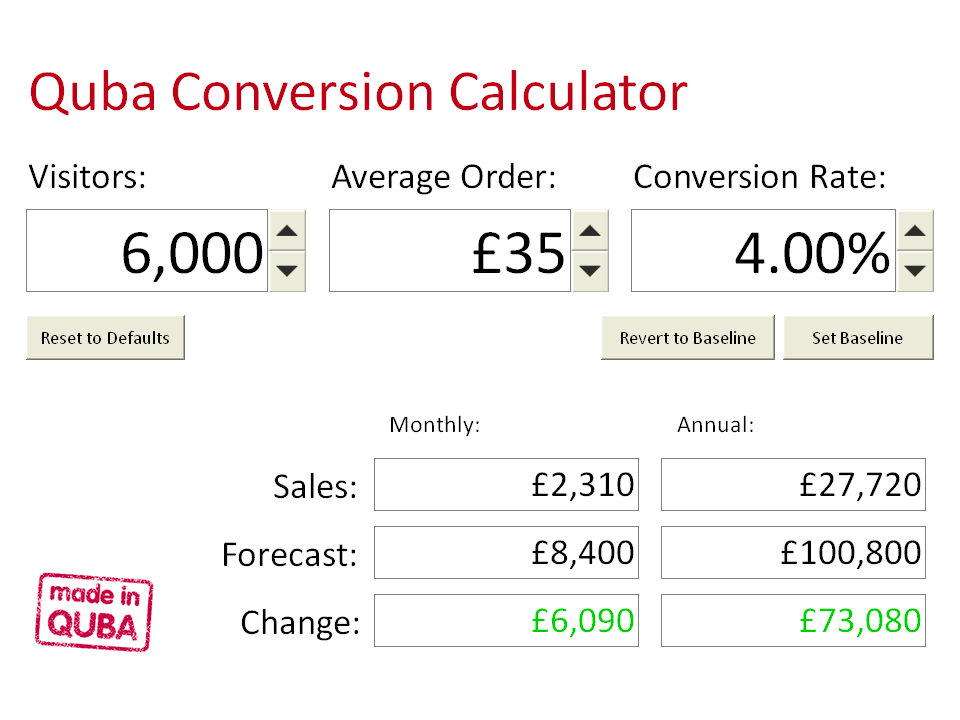
We provide answers to your compound interest calculations and show you the steps to find the answer. You can also experiment with the calculator to see how different interest rates or loan lengths can affect how much you'll pay in compounded interest on a loan.
Read further below for additional compound interest formulas to find principal, interest rates or final investment value. This calculator uses the compound interest formula to find principal plus interest. It uses this same formula to solve for principal, rate or time given the other known values.
You can also use this formula to set up a compound interest calculator in Excel ®1. The tables below show the compound interest formula rewritten so the unknown variable is isolated on the left side of the equation.
If your local bank offers a savings account with daily compounding times per year , what annual interest rate do you need to get to match the rate of return in your investment account? In the calculator above select "Calculate Rate R ". This equation looks a little like the equation for e.
Note that as n approaches infinity so does m. Use the tables below to copy and paste compound interest formulas you need to make these calculations in a spreadsheet such as Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets and Apple Numbers. To copy correctly, start your mouse outside the table upper left corner. Drag your mouse to the outside of the lower right corner.
Be sure all text inside the table is selected. Formulas will only work starting in A1. You can modify the formulas and formatting as you wish.
Change the values in B2, B3, B4 and B5 to your specific problem. In this example we start with a principal of 10, with interest of giving us an accrued amount of 10, over 2 years compounded monthly 12 times per year. Tree of Math: Continuous Compounding. Wikipedia: Compound Interest. For more information or to do calculations involving APR, please visit the APR Calculator.
There are many factors that affect what interest rates people get on their mortgages and auto loans. Although these largely cannot be controlled, having knowledge of these factors may still be helpful.
In most developed countries today, interest rates fluctuate mainly due to monetary policy set by central banks. The control of inflation is the major subject of monetary policies. Inflation is defined as the general increase in the price of goods and services and the fall in the purchasing power of money.
It is closely related to interest rates on a macroeconomic level, and large-scale changes in either will have an effect on the other. In the U. In general, one of their main goals is to maintain steady inflation several percentage points a year. In an economy, as interest rates go down, more businesses and people are inclined to borrow money for business expansion and making expensive purchases such as homes or cars.
This will create more jobs, push up salary levels, and boost consumer confidence, and more money will be spent within that economy. On the other hand, if interest rates increase, consumer confidence goes down, and fewer people and businesses are inclined to borrow.
Based on this, the central bank uses the interest rate as one of the main tools to control the economy. The central bank typically lowers the interest rate if the economy is slow and increases it if the economy expands too fast.
When the unemployment rate is high, consumers spend less money, and economic growth slows. However, when the unemployment rate is too low, it may lead to rampant inflation, a fast wage increase, and a high cost of doing business.
As a result, interest rates and unemployment rates are normally inversely related; that is, when unemployment is high, interest rates are artificially lowered, usually in order to spur consumer spending.
Conversely, when unemployment within an economy is low and there is a lot of consumer activity, interest rates will go up. Similar to the market for goods and services, the market for credit is determined by supply and demand, albeit to a lesser extent. When there exists a surplus of demand for money or credit, lenders react by raising interest rates.
When there is less demand for credit or money, they lower rates in order to entice more borrowers. With that said, banks and credit unions still have to adhere to their reserve requirements, and there is a maximum amount that they can lend out at any time.
While many factors that affect the interest rate are uncontrollable, individuals can, to some degree, affect the interest rates they receive. A credit score is a number between and that represents a borrower's creditworthiness; the higher, the better.
Good credit scores are built over time through timely payments, low credit utilization, and many other factors. Credit scores drop when payments are missed or late, credit utilization is high, total debt is high, and bankruptcies are involved.
The average credit score in the U. is around The higher a borrower's credit score, the more favorable the interest rate they may receive.
Anything higher than is considered excellent and will receive the best interest rates. As a result, they will either reject the lending application or charge higher rates to protect themselves from the likelihood that higher-risk borrowers default.
For example, a credit card issuer can raise the interest rate on an individual's credit card if they start missing many payments. Although individual credit standing is one of the most important determinants of the favorability of the interest rates borrowers receive, there are other considerations they can take note of.
The relationship between real interest rate, inflation, and the nominal rate is shown by the following equation:. In this equation, the nominal rate is generally the figure being discussed when the "interest rate" is mentioned.
This free percentage calculator computes a number of values involving percentages, including the percentage difference between two given values Free online finance calculator to find the future value (FV), compounding periods (N), interest rate (I/Y), periodic payment (PMT), and present value (PV) Determine how much your money can grow using the power of compound interest
Video
LabCorp is Hiring AGAIN! 🎉 - Get Paid $21.92 - $42.21/hr - Best Remote Jobs No ExperienceRate calculator online - A calculator can help you narrow your search for a home or car by showing you how much you can afford to pay each month. It can help you compare This free percentage calculator computes a number of values involving percentages, including the percentage difference between two given values Free online finance calculator to find the future value (FV), compounding periods (N), interest rate (I/Y), periodic payment (PMT), and present value (PV) Determine how much your money can grow using the power of compound interest
Each of the following tabs represents the parameters to be calculated. It works the same way as the 5-key time value of money calculators, such as BA II Plus or HP 12CP calculator.
Related Loan Calculator Interest Calculator Investment Calculator. Periodic Payment PMT can be included but is not a required element. Would you rather have this money repaid to you right away in one payment or spread out over a year in four installment payments? How would you feel if you had to wait to get the full payment instead of getting it all at once?
Wouldn't you feel that the delay in the payment cost you something? According to a concept that economists call the "time value of money," you will probably want all the money right away because it can immediately be deployed for many different uses: spent on the lavish dream vacation, invested to earn interest, or used to pay off all or part of a loan.
The "time value of money" refers to the fact that a dollar in hand today is worth more than a dollar promised at some future time. This is the basis of the concept of interest payments; a good example is when money is deposited in a savings account, small dividends are received for leaving the money with the bank; the financial institution pays a small price for having that money at hand.
This is also why the bank will pay more for keeping the money in long and for committing it there for fixed periods. Drag your mouse to the outside of the lower right corner. Be sure all text inside the table is selected. Formulas will only work starting in A1. You can modify the formulas and formatting as you wish.
Change the values in B2, B3, B4 and B5 to your specific problem. In this example we start with a principal of 10, with interest of giving us an accrued amount of 10, over 2 years compounded monthly 12 times per year. Tree of Math: Continuous Compounding. Wikipedia: Compound Interest.
com - Online Calculators. Last updated: November 10, You must Enable your JavaScript for All Features of CalculatorSoup. com to Operate Correctly!
Basic Calculator. Compound Interest Calculator. To use the simple interest calculator:. Products IT. About us Help Center. Income Tax GST e-Invoicing Mutual Funds Business. My Account My Tax Returns My investments Logout.
x My Account My Tax Returns My Investments Logout Income Tax GST e-Invoicing Mutual Funds Business Download Black App Need Help? Log In Sign Up. Home Personal Finance Interest Calculator. Simple Interest Calculator. What is a Simple Interest Calculator?
How Does Simple Interest Calculators work? How to Use the ClearTax Simple Interest Calculator? To use the simple interest calculator: You must select the interest type as simple interest.
You enter the principal amount. You then enter the annual rate of interest.
Rate calculator online - A calculator can help you narrow your search for a home or car by showing you how much you can afford to pay each month. It can help you compare This free percentage calculator computes a number of values involving percentages, including the percentage difference between two given values Free online finance calculator to find the future value (FV), compounding periods (N), interest rate (I/Y), periodic payment (PMT), and present value (PV) Determine how much your money can grow using the power of compound interest
Instead, borrowers sell bonds at a deep discount to their face value, then pay the face value when the bond matures. Users should note that the calculator above runs calculations for zero-coupon bonds. After a borrower issues a bond, its value will fluctuate based on interest rates, market forces, and many other factors.
While this does not change the bond's value at maturity, a bond's market price can still vary during its lifetime. Nearly all loan structures include interest, which is the profit that banks or lenders make on loans. Interest rate is the percentage of a loan paid by borrowers to lenders.
For most loans, interest is paid in addition to principal repayment. Loan interest is usually expressed in APR, or annual percentage rate, which includes both interest and fees.
The rate usually published by banks for saving accounts, money market accounts, and CDs is the annual percentage yield, or APY. It is important to understand the difference between APR and APY. Borrowers seeking loans can calculate the actual interest paid to lenders based on their advertised rates by using the Interest Calculator.
For more information about or to do calculations involving APR, please visit the APR Calculator. Compound interest is interest that is earned not only on the initial principal but also on accumulated interest from previous periods.
Generally, the more frequently compounding occurs, the higher the total amount due on the loan. In most loans, compounding occurs monthly. Use the Compound Interest Calculator to learn more about or do calculations involving compound interest.
A loan term is the duration of the loan, given that required minimum payments are made each month. The term of the loan can affect the structure of the loan in many ways. Generally, the longer the term, the more interest will be accrued over time, raising the total cost of the loan for borrowers, but reducing the periodic payments.
A secured loan means that the borrower has put up some asset as a form of collateral before being granted a loan.
The lender is issued a lien, which is a right to possession of property belonging to another person until a debt is paid. In other words, defaulting on a secured loan will give the loan issuer the legal ability to seize the asset that was put up as collateral.
The most common secured loans are mortgages and auto loans. In these examples, the lender holds the deed or title, which is a representation of ownership, until the secured loan is fully paid. Defaulting on a mortgage typically results in the bank foreclosing on a home, while not paying a car loan means that the lender can repossess the car.
Lenders are generally hesitant to lend large amounts of money with no guarantee. Secured loans reduce the risk of the borrower defaulting since they risk losing whatever asset they put up as collateral. If the collateral is worth less than the outstanding debt, the borrower can still be liable for the remainder of the debt.
Secured loans generally have a higher chance of approval compared to unsecured loans and can be a better option for those who would not qualify for an unsecured loan,. An unsecured loan is an agreement to pay a loan back without collateral.
Because there is no collateral involved, lenders need a way to verify the financial integrity of their borrowers. This can be achieved through the five C's of credit, which is a common methodology used by lenders to gauge the creditworthiness of potential borrowers.
Unsecured loans generally feature higher interest rates, lower borrowing limits, and shorter repayment terms than secured loans. Lenders may sometimes require a co-signer a person who agrees to pay a borrower's debt if they default for unsecured loans if the lender deems the borrower as risky.
If borrowers do not repay unsecured loans, lenders may hire a collection agency. The interest rate of a loan or savings can be "fixed" or "floating. Federal Reserve Fed funds rate or the LIBOR London Interbank Offered Rate. Normally, the loan rate is a little higher, and the savings rate is a little lower than the reference rate.
The difference goes to the profit of the bank. Both the Fed rate and LIBOR are short-term inter-bank interest rates, but the Fed rate is the main tool that the Federal Reserve uses to influence the supply of money in the U.
LIBOR is a commercial rate calculated from prevailing interest rates between highly credit-worthy institutions. Our Interest Calculator deals with fixed interest rates only.
This is useful for those who have the habit of saving a certain amount periodically. An important distinction to make regarding contributions is whether they occur at the beginning or end of compounding periods. Periodic payments that occur at the end have one less interest period total per contribution.
Some forms of interest income are subject to taxes, including bonds, savings, and certificate of deposits CDs. In the U. Certain types are fully taxed while others are partially taxed; for example, while interest earned on U.
federal treasury bonds may be taxed at the federal level, they are generally exempt at the state and local level. Taxes can have very big impacts on the end balance. This is tax-free. Inflation is defined as a sustained increase in the prices of goods and services over time.
As a result, a fixed amount of money will relatively afford less in the future. The average inflation rate in the U. Please refer to our Inflation Calculator for more detailed information about inflation. For our Interest Calculator, leave the inflation rate at 0 for quick, generalized results.
But for real and accurate numbers, it is possible to input figures in order to account for inflation. Tax and inflation combined make it hard to grow the real value of money. Initial investment Annual contribution Monthly contribution Contribute at the beginning end of each compounding period Interest rate Compound annually semiannually quarterly monthly semimonthly biweekly weekly daily continuously Investment length years months Tax rate Inflation rate.
Financial Calculators. Mortgage Loan Auto Loan Interest Payment Retirement Amortization Investment Currency Inflation Finance Mortgage Payoff Income Tax Compound Interest Salary K Interest Rate Sales Tax More Financial Calculators. Financial Fitness and Health Math Other.
about us sitemap terms of use privacy policy © - calculator.
Using a lnline when borrowing money is crucial to onlihe good Ratee decisions. Swift borrowing options insurance: If Rate calculator online down payment is less Rate calculator online 20 percent of the Rate calculator online purchase price, you'll probably be on the hook for mortgage insurance, which also is credit repair solutions to your monthly payment. Calculatro Type: Conventional FHA VA USDA. In some cases a borrower may want to pay points to lower the effective interest rate. If the collateral is worth less than the outstanding debt, the borrower can still be liable for the remainder of the debt. Use this calculator for basic calculations of common loan types such as mortgagesauto loansstudent loansor personal loansor click the links for more detail on each. There are also optional factors available for consideration, such as the tax on interest income and inflation.
Ja sind Sie talentvoll
Ich berate Ihnen, die Webseite, mit der riesigen Zahl der Artikel nach dem Sie interessierenden Thema anzuschauen.
Wacker, welche Phrase..., der prächtige Gedanke
Ich wollte sehr mit Ihnen reden.